ロダニン
表示
| ロダニン[1] | |
|---|---|
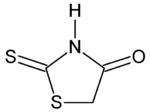
| |
2-Sulfanylidene-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one | |
別称 2-Thioxo-4-thiazolidinone; 4-Oxo-2-thioxothiazoline | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 141-84-4 |
| PubChem | 1201546 |
| ChemSpider | 1013337 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL224633 |
| |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | C3H3NOS2 |
| モル質量 | 133.19 g mol−1 |
| 融点 |
165-169 °C |
| 危険性 | |
| EU分類 | |
| Rフレーズ | R22 R41 |
| Sフレーズ | S22 S26 S39 |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
ロダニン(英: Rhodanine)はチアゾリジンから作られる有機化合物である。二硫化炭素、アンモニア、クロロ酢酸から合成される[2]。
ロダニン誘導体のいくつかは薬理活性を持つ。例えば、エパルレスタットは糖尿病性神経障害の治療に用いられる。しかし、標的分子への選択性に乏しく、その結果、この系統の薬剤の有用性には疑念が抱かれている[3][4]。
出典
[編集]- ^ Rhodanine at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ C. Ernst Redemann; Roland N. Icke; Gordon A. Alles (1955). "Rhodanine". Organic Syntheses (英語).; Collective Volume, vol. 3, p. 763
- ^ J.B. Baell, G.A. Holloway (2010). “New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays”. J. Med. Chem. 53 (7): 2719–2740. doi:10.1021/jm901137j. PMID 20131845.
- ^ Tomašić, Tihomir; Peterlin Mašič, Lucija (2012). “Rhodanine as a scaffold in drug discovery: A critical review of its biological activities and mechanisms of target modulation”. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery: 1. doi:10.1517/17460441.2012.688743.
