利用者:加藤勝憲/内膜
内膜は、動脈・静脈の血管壁の最も内側の膜(層)である。1層の内皮細胞で構成され、内部の弾性ラミナで支えられている。 内皮細胞は血流と直接接触している。It is made up of one layer of endothelial cells and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow.
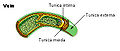
血管の3層とは、内層(内膜)、中間層(中膜)、外層(外膜)である。
The three layers of a blood vessel are an inner layer (the tunica intima), a middle layer (the tunica media), and an outer layer (the tunica externa).
解剖の際、内膜(tunica intima)は中央部(tunica medium)から少し浸軟することによって分離することができる。内膜は細かく無色透明で弾力性に富み、死後は一般に縦皺に波打つ。
In dissection
構造
[編集]The structure of the tunica intima depends on the blood vessel type.[1]
Elastic arteries – A single layer of Endothelial and a supporting layer of elastin-rich collagen. The layer also contains fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells called 'myointimal cells'
Muscular arteries – Endothelial cells
Arterioles – A single layer of Endothelial cells
Veins – Endothelial cells[2]
The inner coat consists of:
- A layer of pavement endothelium, the cells of which are polygonal, oval, or fusiform, and have very distinct round or oval nuclei. This endothelium is brought into view most distinctly by staining with silver nitrate.
- A subendothelial layer, consisting of delicate connective tissue with branched cells lying in the interspaces of the tissue; in arteries of less than 2 mm in diameter the subendothelial layer consists of a single stratum of stellate cells, and the connective tissue is only largely developed in vessels of a considerable size.[要出典]
- An elastic or fenestrated layer, which consists of a membrane containing a network of elastic fibers, having principally a longitudinal direction, and in which, under the microscope, small elongated apertures or perforations may be seen, giving it a fenestrated appearance. It was therefore called by Henle the fenestrated membrane. This membrane forms the chief thickness of the inner coat, and can be separated into several layers, some of which present the appearance of a network of longitudinal elastic fibers, and others a more membranous character, marked by pale lines having a longitudinal direction. In minute arteries the fenestrated membrane is a very thin layer; but in the larger arteries, and especially in the aorta, it has a considerable thickness.
機能
[編集]Endothelium had been seen to be simply the boundary between the blood in the lumen and the walls of the vessels. However, endothelium has been shown to release local chemicals called endothelins which are powerful vasoconstrictors.[3] Endothelins help to regulate capillary exchange and alter blood flow by their constriction of the smooth muscle in the walls. Vasoconstriction increases blood pressure, and its overexpression can contribute to hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
Additional images
[編集]脚注・参考文献
[編集]この記事にはパブリックドメインであるグレイ解剖学第20版(1918年)本文が含まれています。
外部リンク
[編集]- – "Aorta"
- — "Bird, vessels (LM, High)"
[[Category:動脈]]
- ^ Steve, Paxton; Michelle, Peckham; Adele, Knibbs (2003) (英語). The Leeds Histology Guide.
- ^ Steve, Paxton; Michelle, Peckham; Adele, Knibbs (2003) (英語). The Leeds Histology Guide.
- ^ Haryono, A; Ramadhiani, R; Ryanto, GRT; Emoto, N (16 May 2022). “Endothelin and the Cardiovascular System: The Long Journey and Where We Are Going.”. Biology 11 (5): 759. doi:10.3390/biology11050759. PMC 9138590. PMID 35625487.