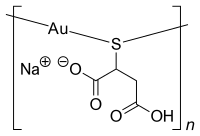
金チオリンゴ酸ナトリウム
 | |
| IUPAC命名法による物質名 | |
|---|---|
| |
| 臨床データ | |
| 販売名 | Myocrisin |
| Drugs.com | |
| ライセンス | US FDA:リンク |
| 胎児危険度分類 | |
| 法的規制 | |
| 薬物動態データ | |
| 血漿タンパク結合 | High[1] |
| 半減期 | 6-25 days[1] |
| 排泄 | Urine (60-90%), faeces (10-40%)[1] |
| データベースID | |
| ATCコード | M01CB01 (WHO) |
| PubChem | CID: 16760302 |
| ChemSpider |
7827788 |
| UNII |
E4768ZY6GM |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:35863 |
| 化学的データ | |
| 化学式 | C4H4AuNaO4S |
| 分子量 | 367.939350590 |
| |
金チオリンゴ酸ナトリウム(Sodium aurothiomalate、Gold sodium thiomalate)は、抗リウマチ薬 として用いられる金化合物である[2][3]。医薬品として用いられている金化合物は、金チオリンゴ酸ナトリウムとオーラノフィンのみである[4]。商品名シオゾール。
効能・効果
[編集]用法・用量
[編集]関節リウマチには毎週または隔週10mg筋肉内投与から開始し、50mgまたは100mgまで増量する。ただしその間に奏効した場合には適当な最低維持量の投与を継続する。
副作用
[編集]最も一般的な副作用は消化器症状(消化不良、腫脹、吐気、嘔吐、味覚異常 等)、血管運動症状(潮紅、失神、眩暈、発汗、脱力感、動悸、息切れ、視覚異常 等)、皮膚症状(瘙痒感、発疹、注射部位刺激、脱毛 等)である。そのほか、結膜炎、血液障害、腎機能障害、関節痛、筋肉痛、肝機能障害も良く知られている[6]。消化管出血、粘膜乾燥、歯肉炎も発現する[6]。また頻度は稀であるが、再生不良性貧血、潰瘍性腸炎、嚥下困難、血管性浮腫、肺炎、肺線維症、肝毒性、胆汁鬱滞性黄疸、末梢神経障害、ギラン・バレー症候群、脳症、脳炎、日光過敏症も発現し得る[6]。
重大な副作用に挙げられているものは、ショック、アナフィラキシー様症状、剥脱性皮膚炎、Stevens-Johnson症候群(皮膚粘膜眼症候群)、再生不良性貧血、血小板減少、白血球減少、無顆粒球症、赤芽球癆、ネフローゼ症候群(膜性腎症等)、間質性肺炎、肺線維症、好酸球性肺炎、気管支炎、気管支喘息発作の増悪、大腸炎(時に劇症)、角膜潰瘍、網膜出血、脳症、末梢性神経障害、ミオキミアである[7]。
作用機序
[編集]詳細な作用機序は不明であるが、プロスタグランジン合成阻害作用があることが判っている[4]。食細胞に働き掛け、MHCクラスII分子-蛋白相互作用を阻害する[4]。以下の酵素を阻害する事も判明している[4][8]。
出典
[編集]- ^ a b c “aurothiomalate, sodium, Myochrysine (gold sodium thiomalate) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more”. Medscape Reference. WebMD. 13 March 2014閲覧。
- ^ Jessop, J. D.; O'Sullivan, M. M.; Lewis, P. A.; Williams, L. A.; Camilleri, J. P.; Plant, M. J.; Coles, E. C. (1998). “A long-term five-year randomized controlled trial of hydroxychloroquine, sodium aurothiomalate, auranofin and penicillamine in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid rthritis”. British journal of rheumatology 37 (9): 992–1002. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/37.9.992. PMID 9783766.
- ^ Iqbal, M. S.; Saeed, M.; Taqi, S. G. (2008). “Erythrocyte Membrane Gold Levels After Treatment with Auranofin and Sodium Aurothiomalate”. Biological Trace Element Research 126 (1–3): 56–64. doi:10.1007/s12011-008-8184-x. PMID 18649049.
- ^ a b c d Kean, WF; Kean, IRL (4 June 2008). “Clinical pharmacology of gold”. Inflammopharmacology 16 (3): 112–125. doi:10.1007/s10787-007-0021-x. PMID 18523733.
- ^ Benedek, TG (January 2004). “The history of gold therapy for tuberculosis.”. Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences 59 (1): 50-89. doi:10.1093/jhmas/jrg042. PMID 15011812.
- ^ a b c Nick Buckley (2013). Australian Medicines Handbook. Adelaide, S. Aust.. ISBN 9780980579093
- ^ “シオゾール注10mg/シオゾール注25mg 添付文書” (2015年11月). 2015年1月6日閲覧。
- ^ Berners-Price, SJ; Filipovska, A (September 2011). “Gold compounds as therapeutic agents for human diseases.”. Metallomics 3 (9): 863-73. doi:10.1039/c1mt00062d. PMID 21755088.
