KLK6
KLK6(カリクレイン6、kallikrein-6)は、ヒトではKLK6遺伝子にコードされるタンパク質である[5][6][7][8]。KLK6は、ニューロシン(neurosin)、protease M、hK6、zymeといった名称でも知られる。16残基のシグナル配列、5残基の活性化ペプチドを含む244アミノ酸のポリペプチドとして合成され、223アミノ酸の成熟型へとプロセシングされる[9]。
機能
[編集]カリクレインは多様な生理機能を有するセリンプロテアーゼのグループである。多くのカリクレインが発がんに関与しており、その一部はがんやその他の疾患のバイオマーカーとなりうることを示唆するエビデンスが蓄積している。KLK6遺伝子にコードされているプレプロタンパク質は、切断されて成熟型プロテアーゼとなる。このプロテアーゼの発現はステロイドホルモンによって調節されており、またヒトの複数種のがんや乾癬患者の血清で上昇している可能性がある。KLK6はアミロイド前駆体タンパク質やα-シヌクレインの切断に関与している可能性があり、そのためアルツハイマー病やパーキンソン病と関連している可能性が示唆されている。KLK6遺伝子は19番染色体上のカリクレイン遺伝子クラスター内に位置している[8]。
構造
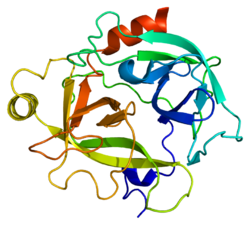
[編集]KLK6の二次構造は、13本のβストランド、2本のαヘリックス、2個の310ヘリックス、8か所のループ領域から構成される。アミノ酸配列の面では、ラットのMyelencephalon-Specific Protease(MSP)[10]と最も類似している。MSPとKLK6はどちらもアルギニン残基の後のペプチド結合を標的とし、また自身のタンパク質内のアルギニンに対する自己切断を行う[11]。
構造の面では、KLK6はウシトリプシンと類似している。基質結合部位近傍のループは短く、結合部位から離れるように位置しており、S2、S3部位の形成にはあまり寄与していないようである。S1部位にはアスパラギン酸、ヒスチジン、セリンの触媒三残基に加えて189–195、214–220、224–228番残基が位置している[12]。
病理
[編集]α-シヌクレインの蓄積は、レビー小体型認知症、パーキンソン病、多系統萎縮症の患者に広くみられる。α-シヌクレインの分解を担うタンパク質の同定のため、プロテアーゼ阻害剤を用いた探索が行われている。さまざまなセリンプロテアーゼ阻害剤(アプロチニン、PMSF、ロイペプチン、AEBSF)が分解経路に大きな影響を及ぼすことから、α-シヌクレインの分解にセリンプロテアーゼが必要であることが示唆されている。カリクレイン阻害剤も用量依存的に分解を阻害し、また精製されたカリクレインがα-シヌクレインに対する分解活性を有することがin vitroで示されている[13]。
KLK6はこうした疾患の防止に寄与している一方、悪性腫瘍細胞の拡散にも寄与している可能性がある。KLK6は分解酵素として、正常細胞や悪性細胞の双方の細胞外マトリックスを分解する能力を有し、遊走能やシグナル伝達能力を高めている可能性がある。KLK6はフィブロネクチン、ラミニン、ビトロネクチン、コラーゲンなどの細胞外マトリックスタンパク質に対する分解活性を有し、またKLK6中和抗体によって処理された腫瘍細胞は遊走能が低下する[14]。
機構
[編集]
KLK6はAsp102、His57、Ser195が触媒三残基を形成し、N末端側にアルギニン残基が位置するペプチド結合を特異的に加水分解する[15]。他のセリンプロテアーゼと類似した触媒機構を有すると考えられている[16]。
- ヒスチジン残基がセリン残基を脱プロトン化する
- セリン残基がアミド結合の代替となる
- プロトン化ヒスチジン残基によってアミンがより良い脱離基となり、オキシアニオンが崩壊してエステルが形成される
- 水分子がエステル結合を切断し、セリン残基が脱離する
出典
[編集]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000167755 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000050063 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ Human PubMed Reference:
- ^ Mouse PubMed Reference:
- ^ “Molecular cloning of a novel trypsin-like serine protease (neurosin) preferentially expressed in brain”. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression 1350 (1): 11–14. (January 1997). doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(96)00187-x. PMID 9003450.
- ^ “A comprehensive nomenclature for serine proteases with homology to tissue kallikreins”. Biological Chemistry 387 (6): 637–641. (June 2006). doi:10.1515/BC.2006.082. PMID 16800724.
- ^ “Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Kallikreins, Lausanne, Switzerland, September 1-3 , 2005”. Biological Chemistry 387 (6): 635–824. (June 2006). doi:10.1515/BC.2006.081. PMID 16800723.
- ^ a b “Entrez Gene: KLK6 kallikrein-related peptidase 6”. 2024年7月14日閲覧。
- ^ “The structure of human prokallikrein 6 reveals a novel activation mechanism for the kallikrein family”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277 (30): 27273–27281. (July 2002). doi:10.1074/jbc.M201534200. PMID 12016211.
- ^ Blaber, Sachiko I.; Scarisbrick, Isobel A.; Bernett, Matthew J.; Dhanarajan, Pushparani; Seavy, Margaret A.; Jin, Yonghao; Schwartz, Martin A.; Rodriguez, Moses et al. (2002-01-29). “Enzymatic properties of rat myelencephalon-specific protease”. Biochemistry 41 (4): 1165–1173. doi:10.1021/bi015781a. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 11802715.
- ^ “Crystal structure and biochemical characterization of human kallikrein 6 reveals that a trypsin-like kallikrein is expressed in the central nervous system” (English). The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277 (27): 24562–24570. (July 2002). doi:10.1074/jbc.M202392200. PMID 11983703.
- ^ “Crystal structure and biochemical characterization of human kallikrein 6 reveals that a trypsin-like kallikrein is expressed in the central nervous system” (English). The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277 (27): 24562–24570. (July 2002). doi:10.1074/jbc.M202392200. PMID 11983703.
- ^ “Alpha-synuclein degradation by serine protease neurosin: implication for pathogenesis of synucleinopathies”. Human Molecular Genetics 12 (20): 2625–2635. (October 2003). doi:10.1093/hmg/ddg283. PMID 12928483.
- ^ “Human kallikrein 6 degrades extracellular matrix proteins and may enhance the metastatic potential of tumour cells” (english). Tumour Biology 25 (4): 193–199. (2004). doi:10.1159/000081102. PMID 15557757.
- ^ “The autolytic regulation of human kallikrein-related peptidase 6”. Biochemistry 46 (17): 5209–5217. (May 2007). doi:10.1021/bi6025006. PMC 2517904. PMID 17417874.
- ^ “Serine protease mechanism and specificity”. Chemical Reviews 102 (12): 4501–4524. (December 2002). doi:10.1021/cr000033x. PMID 12475199.
関連文献
[編集]- “Role of kallikrein enzymes in the central nervous system”. Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry 329 (1–2): 1–8. (March 2003). doi:10.1016/S0009-8981(03)00004-4. PMID 12589961.
- “Value of measuring plasmatic levels of neurosin in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease”. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 14 (1): 59–67. (May 2008). doi:10.3233/JAD-2008-14106. PMID 18525128.
- “Plasmatic level of neurosin predicts outcome of mild cognitive impairment”. International Archives of Medicine 1 (1): 11. (July 2008). doi:10.1186/1755-7682-1-11. PMC 2475518. PMID 18620574.
- “A novel protease homolog differentially expressed in breast and ovarian cancer”. Molecular Medicine 2 (5): 624–636. (September 1996). doi:10.1007/BF03401646. PMC 2230195. PMID 8898378.
- “Zyme, a novel and potentially amyloidogenic enzyme cDNA isolated from Alzheimer's disease brain”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 272 (40): 25135–25142. (October 1997). doi:10.1074/jbc.272.40.25135. PMID 9312124.
- “Molecular characterization of zyme/protease M/neurosin (PRSS9), a hormonally regulated kallikrein-like serine protease”. Genomics 62 (2): 251–259. (December 1999). doi:10.1006/geno.1999.6012. PMID 10610719.
- “Sequencing and expression analysis of the serine protease gene cluster located in chromosome 19q13 region”. Gene 257 (1): 119–130. (October 2000). doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00382-6. PMID 11054574.
- “The spectrum of human kallikrein 6 (zyme/protease M/neurosin) expression in human tissues as assessed by immunohistochemistry”. The Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 49 (11): 1431–1441. (November 2001). doi:10.1177/002215540104901111. PMID 11668196.
- “Crystal structure and biochemical characterization of human kallikrein 6 reveals that a trypsin-like kallikrein is expressed in the central nervous system”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277 (27): 24562–24570. (July 2002). doi:10.1074/jbc.M202392200. PMID 11983703.
- “The structure of human prokallikrein 6 reveals a novel activation mechanism for the kallikrein family”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277 (30): 27273–27281. (July 2002). doi:10.1074/jbc.M201534200. PMID 12016211.
- “Activity of a newly identified serine protease in CNS demyelination”. Brain 125 (Pt 6): 1283–1296. (June 2002). doi:10.1093/brain/awf142. PMID 12023317.
- “Decreased concentration of human kallikrein 6 in brain extracts of Alzheimer's disease patients”. Clinical Biochemistry 35 (3): 225–231. (May 2002). doi:10.1016/S0009-9120(02)00292-8. PMID 12074831.
- “Immunofluorometric quantitation and histochemical localisation of kallikrein 6 protein in ovarian cancer tissue: a new independent unfavourable prognostic biomarker”. British Journal of Cancer 87 (7): 763–771. (September 2002). doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600533. PMC 2364256. PMID 12232761.
- “Decreased cerebrospinal fluid levels of neurosin (KLK6), an aging-related protease, as a possible new risk factor for Alzheimer's disease”. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 977 (1): 216–223. (November 2002). Bibcode: 2002NYASA.977..216M. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04818.x. PMID 12480753.
- “Purification of human kallikrein 6 from biological fluids and identification of its complex with alpha(1)-antichymotrypsin”. Clinical Chemistry 49 (5): 746–751. (May 2003). doi:10.1373/49.5.746. PMID 12709365.
- “Characterization of the enzymatic activity of human kallikrein 6: Autoactivation, substrate specificity, and regulation by inhibitors”. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 307 (4): 948–955. (August 2003). doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)01271-3. PMID 12878203.
- “Alpha-synuclein degradation by serine protease neurosin: implication for pathogenesis of synucleinopathies”. Human Molecular Genetics 12 (20): 2625–2635. (October 2003). doi:10.1093/hmg/ddg283. PMID 12928483.
- “Association of kallikrein expression in nipple aspirate fluid with breast cancer risk”. International Journal of Cancer 108 (4): 588–591. (February 2004). doi:10.1002/ijc.11607. PMID 14696124.
- “Cloning and characterization of novel isoforms of the human kallikrein 6 gene”. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 320 (1): 54–61. (July 2004). doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.04.205. PMID 15207701.