利用者:McYata/sandbox
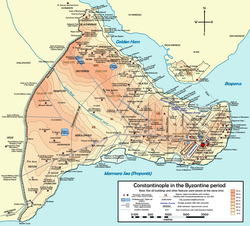
コンスタンティノープル包囲戦の一覧では、現在のトルコ・イスタンブールの一部にあたる地域を占めた都市コンスタンティノープルで行われた歴史上の包囲戦を列挙する。
概要
[編集]コンスタンティノープルは、ヨーロッパ大陸とアジア大陸という2つの大陸と、マルマラ海と黒海という2つの海をつなぐボスポラス海峡のヨーロッパ側に建設された。古代から中世にかけてはシルクロードの結節点として、戦略的にも極めて重要な土地となり、歴史上数多くの国々が征服を試みてきた。
古典古代にビュザンティオンという名で建設されたこの都市が経験した、記録に残る最初の包囲戦は、紀元前510年に発生したオタネス率いるハカーマニシュ朝による攻撃である。この戦いで反乱軍を破ったハカーマニシュ軍はビュザンティオン支配を取り戻したが、その後この町は独立を取り戻した。紀元前70年ごろにローマの支配下にはいりビザンティウムと呼ばれるようになり、自由都市の地位を享受した。しかし五皇帝の年の内戦時に加担する勢力を誤り、193年から196年にかけての包囲戦の末にセプティミウス・セウェルスに敗れ、完全に破壊された。しかしこの地の重要性を認識していたセウェルスは、ビザンティウムを再建した。324年にビザンティウムを征服したコンスタンティヌス1世は、ローマ帝国の首都をローマからこの地に移し、[[]] between 193–196 and was partially sacked during the civil war. After it was captured by Constantine the Great in 324, it became the capital of the Byzantine Empire under the name of New Rome. It later became known as Constantinople and in the years that followed it became under attack by both the Byzantine pretenders fighting for the throne and also by the foreign powers for a total twenty-two times. The city remained under Byzantine rule until the Ottoman Empire took over as a result of the siege in 1453, known as Fall of Constantinople, after which no other sieges took place.
Constantinople was besieged thirty-four times throughout its history. Out of the ten sieges that occurred during its time as a city-state and while it was under Roman rule, six were successful, three were repelled and one was lifted as a result of the agreement between the parties. Three of these sieges were carried out by the Romans who claimed the throne during civil war. Of the twenty-four sieges that took place while it was under Byzantine rule, five were successful, fourteen remained inconclusive, and five were lifted by reaching mutual agreements. Four of these sieges took place during civil wars. The Sack of Constantinople that that took place in 1204 during the Fourth Crusade caused the city to fall and established the Latin Empire. It also sent the Byzantine imperial dynasty to exile, who founded the Empire of Nicaea. Constantinople came under Byzantine rule again in 1261, but was conquered by the Ottomans with the siege in 1453, as a result of which the Byzantine Empire came to an end. The city has been under the rule of Turks since the last siege, except for the period of British rule between 1920–1923.
Sieges
[編集]Notes
[編集]- ^A The "Result" column is relative to the side that carries out the siege.
- ^B While some sources have used Cicero and Tacitus's writings as a reference to argue that the city was in fact under a siege until it "repelled the enemies", other ancient writings found mention that a siege was planned through the sea but didn't take place due to stormy weather conditions.[128][31]
- ^C Byzantine sources give 860 and Russian sources give 866 as the year in which this siege occurred, although it is accepted that the latter is wrong.
- ^D The year in which the siege started is controversial. Fahameddin Başar, Halil İnalcık and Konstantin Josef Jireček gave it as 1394, while Feridun Emecen and Haldun Eroğlu believed that it was 1396. In addition, some sources mention that the siege started in 1391 and ended in 1396, and that between these years, there was only one siege, the severity of which increased and decreased from time to time.[104][113]
References
[編集]- Inline citations
- ^ Herodotos (2012). Tarih. Müntekim Ökmen, çev. (8 ed.). İstanbul: Türkiye İş Bankası Kültür Yayınları. p. 392. ISBN 9789754587210
- ^ Vasilev, Miroslav Ivanov (2015) (英語). The Policy of Darius and Xerxes towards Thrace and Macedonia. Lahey: Brill. p. 86. doi:10.1163/9789004282155. ISBN 9789004282148
- ^ Kuban, Doğan (1993). "Bizantion". Dünden Bugüne İstanbul Ansiklopedisi. Vol. 2. İstanbul: Tarih Vakfı Yayınları. pp. 258–260.
- ^ Yavuz 2014, p. 169.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 1.
- ^ Arslan 2010, p. 78.
- ^ Harris, Jonathan (2017) (英語). Constantinople: Capital of Byzantium (2 ed.). Londra: Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 26. doi:10.1111/j.1540-6563.2009.00246_52.x. ISBN 9781474254656
- ^ Hughes 2017, p. 538.
- ^ Yavuz 2014, p. 191.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 39.
- ^ Arslan, Murat (2011), “Alkibiades'in Khalkhedon ve Byzantion Kuşatması: Nedenleri ve Sonuçları”, in Şahin, Hamdi; Konyar, Erkan; Engin, Gürkan, Özsait Armağanı: Mehmet ve Nesrin Özsait Onuruna Sunulan Makaleler, Antalya: Suna-İnan Kıraç Akdeniz Medeniyetleri Araştırma Enstitüsü, pp. 9-22, ISBN 9786054018093
- ^ Grote, George (2001) (英語). A History of Greece: From the Time of Solon to 403 B.C.. Londra: Routledge. p. 884. ISBN 0415223695
- ^ Hughes 2017, p. 119.
- ^ Yavuz 2014, p. 221.
- ^ Arslan 2010, p. 197.
- ^ Sevin, Veli (2016). Anadolu'nun Tarihi Coğrafyası I (4 ed.). Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Yayınları. p. 24. ISBN 9789751609847
- ^ Hughes 2017.
- ^ Tekin, Oğuz (2001). Byzas'tan I. Constantinus'a Kadar Eskiçağ'da İstanbul (2 ed.). İstanbul: Eskiçağ Bilimleri Enstitüsü Yayınları. p. 33. ISBN 9789757938040
- ^ Yavuz 2014, p. 275.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 81.
- ^ Arslan 2010, p. 233.
- ^ Arslan 2007, p. 56.
- ^ Arslan, Murat (January-February 2014). “Galatların Byzantion Kuşatması”. Aktüel Arkeoloji (İstanbul: Arkeoloji ve Sanat Yayınları) (37): 68-75. ISSN 1307-5756.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 92.
- ^ Arslan 2010, p. 243.
- ^ Yavuz 2014, p. 310.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 129.
- ^ Arslan 2010, p. 343.
- ^ Arslan 2007, p. 334.
- ^ Grillo, Luca (2015) (英語). Cicero's De Provinciis Consularibus Oratio. Londra: Oxford University Press. p. 116. ISBN 9780190224592
- ^ a b Yavuz 2014, p. 344.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 133.
- ^ Arslan 2010, p. 430.
- ^ Hughes 2017, p. 166.
- ^ Freely 2011, p. 109.
- ^ Yavuz 2014, p. 365.
- ^ Sextus Aurelius Victor (1994) (英語). Aurelius Victor: De Caesaribus. H. W. Bird, çev.. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. p. 188. doi:10.3828/978-0-85323-218-6. ISBN 9780853232186
- ^ Gibbon, Edward (1988). Roma İmparatorluğu'nun Gerileyiş ve Çöküş Tarihi. I. Asım Baltacıgil, çev.. İstanbul: Bilim, Felsefe, Sanat Yayınları. p. 444
- ^ Freely 2011, p. 318.
- ^ "İstanbul". Meydan Larousse. Vol. 10. İstanbul: Sabah. 1992. p. 77.
- ^ Yavuz 2014, p. 387.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 153.
- ^ Norwich 2013a, p. 45.
- ^ Hughes 2017, p. 231.
- ^ Yavuz 2014, p. 393.
- ^ Alexander Van Millingen (31 October 2010). Byzantine Constantinople: The Walls of the City and Adjoining Historical Sites. Cambridge University Press. pp. 40–. ISBN 978-1-108-01456-4 19 August 2013閲覧。
- ^ Stephen Turnbull (21 August 2012). The Walls of Constantinople AD 324-1453. Osprey Publishing. pp. 5–. ISBN 978-1-78200-224-6 19 August 2013閲覧。
- ^ Jane Penrose (2005). Rome and Her Enemies: An Empire Created and Destroyed by War. Osprey Publishing. pp. 269–. ISBN 978-1-84176-932-5 19 August 2013閲覧。
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 95.
- ^ Norwich 2013a, p. 240.
- ^ Reazaei, Iman S. (September 2016). “V.-VII. Yüzyıllarda Bizans-Sâsânî İlişkileri”. İraniyat Dergisi (Ankara: İranoloji Derneği Yayınları) (1): 18-31.
- ^ O'Sullivan, Shaun (2004-01-01). “Sebeos' account of an Arab attack on Constantinople in 654”. Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies 28 (1): 67–88. doi:10.1179/byz.2004.28.1.67. ISSN 0307-0131.
- ^ Hoyland, Robert G. (2014-01-01) (英語). In God's Path: The Arab Conquests and the Creation of an Islamic Empire. Oxford University Press. pp. 107. ISBN 9780199916368
- ^ Jankowiak, Marek (2013), “The first Arab siege of Constantinople”, in Zuckerman, Constantin (英語), Travaux et Mémoires Tome XVII - Constructing the Seventh Century, Paris: Association des Amis du Centre d’Histoire et Civilisation de Byzance, pp. 237-320, ISBN 9782916716459
- ^ Apak, Adem (July 2009). “Emevîler Döneminde Anadolu'da Arap-Bizans Mücadelesi”. Uludağ Üniversitesi İlahiyat Fakültesi Dergisi (Bursa: Uludağ Üniversitesi İlahiyat Fakültesi) 18 (2): 104. ISSN 1301-3394.
- ^ Unan, Fahri (14 September 2009). “Müslümanlar ve İstanbul”. hacettepe.edu.tr. 25 August 2017時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。26 August 2017閲覧。
- ^ Uçar, Şahin (1990). Anadolu'da İslâm-Bizans Mücadelesi. İstanbul: İşaret Yayınları. p. 82
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 249.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 115.
- ^ Norwich 2013a, p. 263.
- ^ Hitti, Philip K. (1989). Siyâsî ve Kültürel İslam Tarihi. II. Salih Tuğ, çev.. İstanbul: Boğaziçi Yayınları. p. 320
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 144.
- ^ Hughes 2017, p. 1283.
- ^ Sumner, Graham V. (1976). “Philippicus, Anastasius II and Theodosius III” (英語). Greek, Roman, and Byzantine Studies (Durham, North Carolina: Duke University Department of Classical Studies) 17 (3): 287-294. ISSN 2159-3159. OCLC 6415521.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 253.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 145.
- ^ Norwich 2013a, p. 286.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 265.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 188.
- ^ Vasiliev 2016, p. 326.
- ^ Norwich 2013b, p. 28.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 192.
- ^ Vasiliev 2016, p. 319.
- ^ Norwich 2013b, p. 40.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 282.
- ^ Vasiliev 2016, p. 322.
- ^ Norwich 2013b, p. 66.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 287.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 241.
- ^ Vasiliev 2016, p. 369.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 289.
- ^ Vasiliev 2016, p. 371.
- ^ Norwich 2013b, p. 129.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 308.
- ^ Norwich 2013b, p. 248.
- ^ Hughes 2017, p. 1289.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 341.
- ^ Vasiliev 2016, p. 518.
- ^ Freely 2011, p. 159.
- ^ Demirkent, Işın (1997). Haçlı Seferleri. İstanbul: Dünya Yayıncılık. p. 172. ISBN 9757632546
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 386.
- ^ Vasiliev 2016, p. 520.
- ^ Robert de Clari (1994). İstanbul'un Zaptı (1204). Beynun Akyavaş, çev.. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Yayınları. p. VI
- ^ Ayönü, Yusuf (July 2015). “IV. Haçlı Seferi’nin Ardından Batı Anadolu'da Mücadele Eden İki Rakip: İstanbul Latin Krallığı ve İznik İmparatorluğu”. Cihannüma: Tarih ve Coğrafya Araştırmaları Dergisi (İzmir: İzmir Katip Çelebi Üniversitesi Sosyal ve Beşeri Bilimler Fakültesi) 1 (1): 13. ISSN 2149-0678.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 349.
- ^ a b Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 405.
- ^ Vasiliev 2016, p. 592.
- ^ Georgios Akrapolites (2008). Vekayinâme. Bilge Umar, çev.. İstanbul: Arkeoloji ve Sanat Yayınları. p. 162. ISBN 9786053960935
- ^ Hughes 2017, p. 1296.
- ^ Freely 2011, p. 168.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 499.
- ^ Hughes 2017, p. 1298.
- ^ Baştav 1989, p. 74.
- ^ a b Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 387.
- ^ Eroğlu, Haldun (2004). “Osmanlıların 1453 Öncesi İstanbul Kuşatmaları”. Tarih Araştırmaları Dergisi (Ankara: Ankara Üniversitesi Dil ve Tarih Coğrafya Fakültesi) 22 (35): 89-101. doi:10.1501/Tarar_0000000188. ISSN 1015-1826.
- ^ Demirkent, Işın (2001). "İstanbul". İslâm Ansiklopedisi. Vol. 23. İstanbul: Türkiye Diyanet Vakfı Yayınları. pp. 205–212.
- ^ Baştav 1989, p. 83.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 506.
- ^ İnalcık 2014, p. 68.
- ^ İnalcık, Halil (1992). "Bayezid I". İslâm Ansiklopedisi. Vol. 5. İstanbul: Türkiye Diyanet Vakfı Yayınları. pp. 231–234.
- ^ Emecen, Feridun (2002). "Osmanlı Devleti'nin Kuruluşundan Fetret Dönemine". Türkler Ansiklopedisi. Vol. 9. Ankara: Yeni Türkiye Yayınları. p. 48. ISBN 9789756782330。
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 390.
- ^ a b Yinanç, Mükrimin Halil (1979). "Bayezid I". İslâm Ansiklopedisi. Vol. 2. İstanbul: Millî Eğitim Bakanlığı Devlet Kitapları Müdürlüğü. pp. 369–392.
- ^ Taeschner, Franz (1990). Necmi Ülker, çev.. “1453 Yılına Kadar Osmanlı Türkleri”. Tarih İncelemeleri Dergisi (İzmir: Ege Üniversitesi Edebiyat Fakültesi Tarih Bölümü) 5 (1): 296. ISSN 0257-4152.
- ^ Baştav 1989, p. 91.
- ^ Arslan & Kaçar 2017, p. 393.
- ^ Cezar, Mustafa (2010). Mufassal Osmanlı Tarihi. I. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Yayınları. p. 233. ISBN 9789751623225
- ^ Başar, Fahameddin (2006). "Mûsâ Çelebi". İslâm Ansiklopedisi. Vol. 31. İstanbul: Türkiye Diyanet Vakfı Yayınları. pp. 216–217. ISBN 9753894279。
- ^ Tekirdağ, Şehabeddin (1979). "Mûsâ Çelebî". İslâm Ansiklopedisi. Vol. 8. İstanbul: Millî Eğitim Bakanlığı Devlet Kitapları Müdürlüğü. pp. 661–666.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 2015, p. 515.
- ^ İnalcık 2014, p. 105.
- ^ İnalcık, Halil (1979). "Murad II". İslâm Ansiklopedisi. Vol. 8. İstanbul: Millî Eğitim Bakanlığı Devlet Kitapları Müdürlüğü. p. 600.
- ^ Vasiliev 2016, p. 714.
- ^ Yeorgios Francis (1992). Şehir Düştü. Kriton Dinçmen, çev.. İstanbul: İletişim Yayınları. p. 98. ISBN 9754702837
- ^ Barbaro, Nicolò (2007). Konstantiniye'den İstanbul'a. Muharrem Tan, çev.. İstanbul: Moralite Yayınları. p. 183. ISBN 9789756397961
- ^ Âşık Paşazâde (2003). Osmanoğulları'nın Tarihi. Kemal Yavuz; M. A. Yekta Saraç, çev.. İstanbul: Koç Kültür Sanat Tanıtım. p. 222. ISBN 975296043X
- ^ Ak, Mahmut; Başar, Fahameddin (2010). İstanbul'un Fetih Günlüğü (2 ed.). İstanbul: Çamlıca Basım Yayın. p. 47. ISBN 9789944905961
- ^ Arslan, Murat (2007). Mithradates VI Eupator: Roma'nın Büyük Düşmanı. İstanbul: Odin Yayıncılık. p. 334. ISBN 9789120219790
- Sources
- Arslan, Murat (2010), İstanbul'un Antikçağ Tarihi: Klasik ve Hellenistik Dönemler, İstanbul: Odin Yayıncılık, ISBN 9759078015
- Arslan, Murat; Kaçar, Turhan (2017), Byzantion'dan Constantinopolis'e İstanbul Kuşatmaları, İstanbul: İstanbul Araştırmaları Enstitüsü, ISBN 9786054642670
- Baştav, Şerif (1989), Bizans İmparatorluğu Tarihi: Son Devir (1261-1461), Ankara: Türk Kültürünü Araştırma Enstitüsü Yayınları, ISBN 9754560242
- Freely, John (2011), Troya Savaşı'ndan İstiklal Harbi'ne Anadolu'da Yunanlar, Gül Çağalı Güven, çev., İstanbul: Doğan Kitap, ISBN 9786050904345
- Hughes, Bettany (2017) (英語), Istanbul: A Tale of Three Cities, Londra: Weidenfeld & Nicolson, ISBN 9780297868491
- İnalcık, Halil (2014), Devlet-i 'Aliyye (54 ed.), İstanbul: Türkiye İş Bankası Kültür Yayınları, ISBN 9789944886451
- Norwich, John Julius (2013a), Bizans: Erken Dönem (MS 323-802), 1, Hamide Koyukan, çev., İstanbul: Kabalcı Yayınevi, ISBN 9786055093013
- Norwich, John Julius (2013b), Bizans: Yükseliş Dönemi (MS 803-1081), 2, Selen Hırçın Riegel, çev., İstanbul: Kabalcı Yayınevi, ISBN 9786055093020
- Ostrogorsky, Georg (2015), Bizans Devleti Tarihi, Fikret Işıltan, çev. (8 ed.), Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Yayınları, ISBN 9789751603487
- Vasiliev, Alexander A. (2016), Bizans İmparatorluğu Tarihi, Tevabil Alkaç, çev., İstanbul: Alfa Yayınları, ISBN 9786051712659
- Yavuz, Mehmet Fatih (2014), Byzantion: Byzas'tan Constantinus'a Antik İstanbul, İstanbul: İstanbul Araştırmaları Enstitüsü, ISBN 9786054642304
