利用者:ガンマゼータ/sandbox
| (以下の事項に関する題材の一部) |
| アメリカ合衆国の文化 |
|---|
 |
| 歴史 |
| 住民 |
| 料理 |
| 宗教 |
| スポーツ |
アメリカ合衆国の文化は主として西洋であるが、ネイティブアメリカンやアフリカ、 アジア、ポリネシア、ラテンアメリカの文化に影響を受けている。アメリカの文化と言われるものの要素は、オセアニアやヨーロッパだけでなく、今日のアメリカ合衆国本土である地域へアジアからパレオ・インディアンが流入した1万年以上前に形成し始めた。アメリカ合衆国は、方言や音楽、芸術、社会傾向、料理、そして伝承というような独自かつ特有の社会的・文化的特徴を持つ。アメリカ合衆国は、原住民と入植者、移民の間で出生率・死亡率が異なる上に、建国以来続いてきた民族的・人種的に異なる多くの国からの大規模な人口流入の結果として、民族的・人種的に多様な国家である[1]。
早期の主なヨーロッパの影響は、イギリス統治中に植民地アメリカへのイングランドやスコットランド、ウェールズ、アイルランド系の移民からもたらされた。英語や法体系やその他アメリカに継承された文化を普及させたイギリスとの植民地としてのつながりにより、イギリス文化にアメリカ文化の根幹に存在する影響がある。その他の重要な影響はヨーロッパのその他の地域、特にドイツ[2]とフランスとイタリアに由来する。[要出典]
ジェファーソン流民主主義などのアメリカ特有の要素も大きな役割を果たす[3]。トーマス・ジェファーソンの『バージニア州に関する手記』は、アメリカ国内の創造性が劣化したとする支配的なヨーロッパの総意に対する反動的な言論であり、おそらくアメリカ人の手による初めての影響力の大きい国内に向けた文化的論評であった。[3]。
アメリカの文化には保守的要素と進歩的要素の両方や、科学と宗教の競争、政治機構、リスクテークと自由な表現、物質主義、道徳的要素が含まれる。首尾一貫したイデオロギーの原理があるにも関わらず(例えば個人主義や平等主義、自由への信頼、民主主義)、アメリカの文化は、国土の広さや人種の多様さのため、様々な顔を持つ。アメリカの文化が柔軟でかつ高い象徴性を持つため、アメリカ文化を 神話的アイデンティティと分類した研究者もいる[4]。それをアメリカ例外主義と見る向きもある。[要出典]
アメリカ先住民が発端となった要素やその他の民族の文化―多くはアフリカ系アメリカ人の文化とラテンアメリカの文化、アジア系アメリカ人の文化―も含む。多くのアメリカの文化、特に大衆文化に属するものは、近代のマスメディアを通じて世界中広まった。
アメリカ合衆国は伝統的にるつぼとみなされてきたが、1960年代から今日にかけては、代わりに文化的多様性や多元主義、サラダボウルのイメージに傾いている[5][6][7]。アメリカ文化の広がりのために、アメリカ合衆国国内には平等だが独自性を持つ多くの社会的サブカルチャーがある。アメリカ合衆国における文化的な関係や個人は一般に社会階級や政治的姿勢、宗教的背景や職業や所属する民族集団のような多数の人口統計的特性に依拠する[1]。
地域による差異
[編集]やや異なる文化を持つアメリカ合衆国の地域には、ニューイングランドや中部大西洋岸諸州、アメリカ合衆国南部、アメリカ合衆国中西部、アメリカ合衆国西部―地方の文化に基づき、太平洋諸州やアメリカ合衆国山岳部とさらに細分化することが出来る地域―がある。
カリフォルニアとオレゴン、ワシントンからなるアメリカ合衆国本土の西海岸は、左に偏った政治的志向と社会自由主義的傾向を指して、左海岸とも称されることがある。
アメリカ合衆国南部は、地域の文化の重要な一部をなす社会保守主義的福音主義的プロテスタンティズムのために、非公式に「バイブル・ベルト」と呼ばれ、そこではそれらの宗派での礼拝出席者数は概して米国平均よりも高い。この地域は通常、アメリカ合衆国北東部のメインライン・プロテスタンティズムとカトリシズム、宗教が多様な中西部と五大湖、ユタ州とアイダホ州南部にかけてのモルモン回廊、比較的無宗教なアメリカ合衆国西部と対比される。無宗教の人の割合は北部のバーモント州で最大で34%であり、対してバイブル・ベルトのアラバマ州は6%である [8]。
強烈な文化的差異には、南北戦争前の南部の奴隷社会に代表される米国における長い歴史がある。社会にかぎらず、北部諸州と南部諸州の間の経済的緊張も大変張り詰めていたため、ついには南部がアメリカ連合国として独立宣言を布告する事態となった。かようにして南北戦争が始まったのであった[9]。
フィッシャーの理論
[編集]デイビッド・ハケット・フィッシャーは、今日のアメリカ合衆国が4つの異なる地域の文化から成り立っていることを理論化している[10]。本の主眼は、17、18世紀にイギリスやアイルランドの異なる地域からイギリスのアメリカ植民地に移住したブリテン諸島に由来する4つの入植者グループの風俗に向けられている。フィッシャーの理論は、グループのそれぞれの文化と風俗は時とともに少々の変化があったとしても存続し、米国の4つの現代の地域の文化の基礎となっているというものである。
フィッシャーによれば、アメリカ文化の礎は、イギリス諸島の4つの異なる地域からの、4つに区分できる社会的宗教的グループによる、4回に渡る大移住から築かれた。ニューイングランドの最初期の入植は、ほとんどがイースト・アングリア出身であるピューリタンが入植した1629年から1640年の間に起こり、ニューイングランド地方の文化を築いた。次の大移住は、1640年から1675年までの間にあったイングランド南部の王党派及びアイルランド人とスコットランド人の家事使用人のチェサピーク湾地域への入植であった。
その後、(1675年から1625年の間に)、数千人ものアイルランド人やイングランド人、ドイツ人のクエーカーが、ウィリアム・ペンに率いられ、デラウェア・バレーに入植した。この入植は結果として、今日「ドイツ系アメリカ」文化とされるものの成立に繋がったが、フィッシャーによれば、それは今日では中部大西洋の州から太平洋沿岸まで米国の多くに遍在するとしても、実際には単なる地域的なアメリカ文化である、 最後に、イギリスやアイルランドの国境からやってきたスコットランド系アイルランド人やイングランド人、スコットランド人の入植者は、1717年から1775年の間にアパラチアに入植した。移民によりアップランドサウスの地域文化が成立し、その文化は以来テキサス西部やアメリカ合衆国南西部の一部などの西の地域に広がりを見せた。
フィッシャーは、今日のアメリカ合衆国は1つの一般的なアメリカ文化と3つ以上の地域別下位文化を持つ国家ではないと示唆している。 彼は米国が紛れも無く地域文化によって成り立ち、またそれを理解することは、現代のアメリカの生活にまつわる多くの事物を理解する助けになると断言する。フィッシャーはまた、これらの地域文化の発展は、入植者が最初に来たまさにその場所だけでなく、その来た時期にも由来すると主張する。フィッシャーは、異なる時代では、人々は全く異なる信念、恐れ、希望、そして偏見を持ち、多様な入植者のグループが新世界にそれらの感情を持ち込み、自分の生まれ故郷では変わってしまっても、アメリカでは多かれ少なかれその時点で時が止まってそのまま残されたのだと断言する。
ウッダードの理論
[編集]フィッシャーの業績に続き、コリン・ウッダードは、自著『American Nations』において[11]、北アメリカの11の地域に最初に入植した人々の文化的特質に基づき、これら地域の対抗文化の存在を主張している。これら地域とは、すなわちニューイングランド、ニューネーデルラント、中部、海岸地帯、アパラチア、ディープサウス、ニューフランス、エルノルテ、西海岸、ファーウェスト・ファーストネーション(カナダ北部とアラスカ、そしてグリーンランドからなる地域)である。
ウッダードによると、これら地域は、形式的な州境やあるいは国境ですら越え、無視する。例えば、彼はメキシコの国境をベルリンの壁と比較し、「ある意味で、エルノルテは冷戦中のドイツと似ている。つまり、同じ文化を持つ2つの民族が大きな壁で隔てられているのだ。」と述べた。
Language
[編集]Although the United States has no official language at the federal level, 28 states have passed legislation making English the official language and it is considered to be the de facto national language. According to the 2000 U.S. Census, more than 97% of Americans can speak English well, and for 81% it is the only language spoken at home. More than 300 languages besides English have native speakers in the United States—some of which are spoken by the indigenous peoples (about 150 living languages) and others imported by immigrants.
Spanish has official status in the commonwealth of Puerto Rico and the state of New Mexico; Spanish is the primary spoken language in Puerto Rico and various smaller linguistic enclaves.[12] According to the 2000 census, there are nearly 30 million native speakers of Spanish in the United States. Bilingual speakers may use both English and Spanish reasonably well but code-switch according to their dialog partner or context. Some refer to this phenomenon as Spanglish.
Indigenous languages of the United States include the Native American languages, which are spoken on the country’s numerous Indian reservations and Native American cultural events such as pow wows; Hawaiian, which has official status in the state of Hawaii; Chamorro, which has official status in the commonwealths of Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands; Carolinian, which has official status in the commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands; and Samoan, which has official status in the commonwealth of American Samoa. American Sign Language, used mainly by the deaf, is also native to the country.
The national dialect is known as American English, which itself consists of numerous regional dialects but has some shared unifying features that distinguish it from other national varieties of English. There are four large dialect regions in the United States—the North, the Midland, the South, and the West—and several smaller dialect regions such as those of New York City and Boston. A standard dialect called "General American" (analogous in some respects to the received pronunciation elsewhere in the English-speaking world), lacking the distinctive noticeable features of any particular region, is believed by some to exist as well; it is sometimes regionally associated with the vaguely-defined "Midwest".
Native language statistics for the United States
[編集]The following information is an estimation as actual statistics constantly vary.
According to the CIA,[13] the following is the percentage of total population's native languages in the United States:
- English (82.1%)
- Spanish (10.7%)
- Other Indo-European languages (3.8%)
- Other Asian or Pacific Islander languages (2.7%)
- Other languages (0.7%)
Literature
[編集]
The right to freedom of expression in the American constitution can be traced to German immigrant John Peter Zenger and his legal fight to make truthful publications in the Colonies a protected legal right,en:Template:Relevance-inline ultimately paving the way for the protected rights of American authors.[14][15]
In the eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, American art and literature took most of its cues from Europe. During its early history, America was a series of British colonies on the eastern coast of the present-day United States. Therefore, its literary tradition begins as linked to the broader tradition of English literature. However, unique American characteristics and the breadth of its production usually now cause it to be considered a separate path and tradition.[要出典]
America's first internationally popular writers were James Fenimore Cooper and Washington Irving in the early nineteenth century. They painted an American literary landscape full of humor and adventure. These were followed by Nathaniel Hawthorne, Edgar Allan Poe, Herman Melville, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow and Henry David Thoreau who established a distinctive American literary voice in the middle of the nineteenth century.
Mark Twain, Henry James, and poet Walt Whitman were major figures in the century's second half; Emily Dickinson, virtually unknown during her lifetime, would be recognized as America's other essential poet. Eleven U.S. citizens have won the Nobel Prize in Literature, including John Steinbeck, William Faulkner, Eugene O'Neill, Pearl S. Buck, T. S. Eliot and Sinclair Lewis. Ernest Hemingway, the 1954 Nobel laureate, is often named as one of the most influential writers of the twentieth century.[16]
A work seen as capturing fundamental aspects of the national experience and character—such as Herman Melville's Moby-Dick (1851), Twain's The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn (1885), and F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby (1925)—may be dubbed the "Great American Novel". Popular literary genres such as the Western and hardboiled crime fiction were developed in the United States.
Fine arts
[編集]In the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, American artists primarily painted landscapes and portraits in a realistic style. A parallel development taking shape in rural America was the American craft movement, which began as a reaction to the Industrial Revolution. Developments in modern art in Europe came to America from exhibitions in New York City such as the Armory Show in 1913. After World War II, New York emerged as a center of the art world. Painting in the United States today covers a vast range of styles. American painting includes works by Jackson Pollock, John Singer Sargent, and Norman Rockwell, among many others.
Architecture
[編集]Architecture in the United States is regionally diverse and has been shaped by many external forces, not only English. U.S. architecture can therefore be said to be eclectic, something unsurprising in such a multicultural society.[17] In the absence of a single large-scale architectural influence from indigenous peoples such as those in Mexico or Peru, generations of designers have incorporated influences from around the world. Currently, the overriding theme of American Architecture is modernity, as manifest in the skyscrapers of the 20th century.
Early Neoclassicism accompanied the Founding Father's idealization of European Enlightenment, making it the predominant architectural style for public buildings and large manors. However, in recent years, suburbanization and mass migration to the Sun Belt has allowed architecture to reflect a Mediterranean style as well.[要出典]##
Theater
[編集]この節の加筆が望まれています。 |
Theater of the United States is based in the Western tradition and did not take on a unique dramatic identity until the emergence of Eugene O'Neill in the early twentieth century, now considered by many to be the father of American drama. O'Neill is a four-time winner of the Pulitzer Prize for drama and the only American playwright to win the Nobel Prize for literature. After O'Neill, American drama came of age and flourished with the likes of Arthur Miller, Tennessee Williams, Lillian Hellman, William Inge, and Clifford Odets during the first half of the twentieth century. After this fertile period, American theater broke new ground, artistically, with the absurdist forms of Edward Albee in the 1960s.
Social commentary has also been a preoccupation of American theater, often addressing issues not discussed in the mainstream. Writers such as Lorraine Hansbury, August Wilson, David Mamet and Tony Kushner have all won Pulitzer Prizes for their polemical plays on American society. The United States is also the home and largest exporter of modern musical theater, producing such musical talents as Rodgers and Hammerstein, Lerner and Loewe, Cole Porter, Irving Berlin, Leonard Bernstein, George and Ira Gershwin, Kander and Ebb, and Stephen Sondheim. Broadway is one of the largest theater communities in the world and is the epicenter of American commercial theater.
Dance
[編集]The United States is represented by various genres of dance, from ballet to hip-hop.
Music
[編集]en:Template:Further en:Template:Further

American music styles and influences (such as country, jazz, rock and roll, rock, hip-hop, rap) and music based on them can be heard all over the world. Music in the U.S. is diverse. It includes African-American influence in the 20th century. The first half of this century is famous for jazz, introduced by African-Americans in the south. In the 1960s, 1970s, 1980s, and 1990s, rock was prevalent.
Cinema
[編集]The cinema of the United States, often generally referred to as Hollywood, has had a profound effect on cinema across the world since the early twentieth century. Its history can be separated into four main periods: the silent film era, classical Hollywood cinema, New Hollywood, and the contemporary period. While the Lumiere Brothers are generally credited with the birth of modern cinema, it is American cinema that has emerged as the most dominant force in the industry.
American independent cinema was revitalized in the late 1980s and early 1990s when another new generation of moviemakers, including Spike Lee, Steven Soderbergh, Kevin Smith, and Quentin Tarantino made movies like, respectively: Do the Right Thing; Sex, Lies, and Videotape; Clerks; and Reservoir Dogs. In terms of directing, screenwriting, editing, and other elements, these movies were innovative and often irreverent, playing with and contradicting the conventions of Hollywood movies. Furthermore, their considerable financial successes and crossover into popular culture reestablished the commercial viability of independent film. Since then, the independent film industry has become more clearly defined and more influential in American cinema. Many of the major studios have capitalized on this by developing subsidiaries to produce similar films; for example Fox Searchlight Pictures.
To a lesser degree in the early 21st century, film types that were previously considered to have only a minor presence in the mainstream movie market began to arise as more potent American box office draws. These include foreign-language films such as Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon and Hero and documentary films such as Super Size Me, March of the Penguins, and Michael Moore's Bowling for Columbine and Fahrenheit 9/11.
Broadcasting
[編集]
Science and technology
[編集]en:Template:unreferenced section en:Template:further2

There is a regard for scientific advancement and technological innovation in American culture, resulting in the flow of many modern innovations. The great American inventors include Robert Fulton (the steamboat); Samuel Morse (the telegraph); Eli Whitney (the cotton gin, interchangeable parts); Cyrus McCormick (the reaper); and Thomas Edison (with more than a thousand inventions credited to his name). Most of the new technological innovations over the 20th and 21st centuries were either first invented in the United States and/or first widely adopted by Americans. Examples include the lightbulb, the airplane, the transistor, the atomic bomb, nuclear power, the personal computer, the iPod, video games and online shopping, as well as the development of the Internet.
This propensity for application of scientific ideas continued throughout the 20th century with innovations that held strong international benefits. The twentieth century saw the arrival of the Space Age, the Information Age, and a renaissance in the health sciences. This culminated in cultural milestones such as the Apollo moon landings, the creation of the Personal Computer, and the sequencing effort called the Human Genome Project.
Throughout its history, American culture has made significant gains through the open immigration of accomplished scientists. Accomplished scientists include: Scottish-American scientist Alexander Graham Bell, who developed and patented the telephone and other devices; German scientist Charles Steinmetz, who developed new alternating-current electrical systems in 1889; Russian scientist Vladimir Zworykin, who invented the motion camera in 1919; Serb scientist Nikola Tesla who patented a brushless electrical induction motor based on rotating magnetic fields in 1888. With the rise of the Nazi party in Germany, a large number of Jewish scientists fled Germany and immigrated to the country, one of them being a Jewish theoretical physicist Albert Einstein in the year 1933.
In the years during and following WWII, several innovative scientists immigrated to the U.S. from Europe, such as Enrico Fermi, who came from Italy in 1938 and led the work that produced the world's first self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. Post-war Europe saw many of its scientists, such as rocket scientist Wernher von Braun, recruited by the United States as part of Operation Paperclip.en:Template:Relevance-inline
Education
[編集]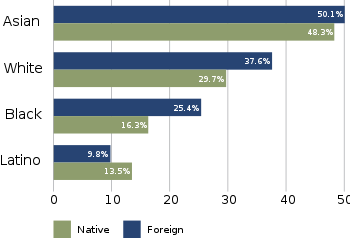
Education in the United States is and has historically been provided mainly by government, with control and funding coming from three levels: federal, state, and local. School attendance is mandatory and nearly universal at the elementary and high school levels (often known outside the United States as the primary and secondary levels).
Students have the options of having their education held in public schools, private schools, or home school. In most public and private schools, education is divided into three levels: elementary school, junior high school (also often called middle school), and high school. In almost all schools at these levels, children are divided by age groups into grades. Post-secondary education, better known as "college" in the United States, is generally governed separately from the elementary and high school system.
In the year 2000, there were 76.6 million students enrolled in schools from kindergarten through graduate schools. Of these, 72 percent aged 12 to 17 were judged academically "on track" for their age (enrolled in school at or above grade level). Of those enrolled in compulsory education, 5.2 million (10.4 percent) were attending private schools. Among the country's adult population, over 85 percent have completed high school and 27 percent have received a bachelor's degree or higher.[要出典]
Religion
[編集]
Among developed countries, the U.S. is one of the most religious in terms of its demographics. According to a 2002 study by the Pew Global Attitudes Project, the U.S. was the only developed nation in the survey where a majority of citizens reported that religion played a "very important" role in their lives, an opinion similar to that found in Latin America.[18] Today, governments at the national, state, and local levels are a secular institution, with what is often called the "separation of church and state".
Although participation in organized religion has been diminishing, the public life and popular culture of the United States incorporates many Christian ideals specifically about redemption, salvation, conscience, and morality. Examples are popular culture obsessions with confession and forgiveness, which extends from reality television to twelve-step meetings. Americans expect public figures to confess and have public penitence for any sins, or moral wrongdoings they may have caused. According to Salon, examples of inadequate public penitence may include the scandals and fallout regarding Tiger Woods, Alex Rodriguez, Mel Gibson, Larry Craig, and Lance Armstrong.[19]

Several of the original Thirteen Colonies were established by English and Irish settlers who wished to practice their own religion without discrimination or persecution: Pennsylvania was established by Quakers, Maryland by Roman Catholics, and the Massachusetts Bay Colony by Puritans. Separatist Congregationalists (Pilgrim Fathers) founded Plymouth Colony in 1620. They were convinced that the democratic form of government was the will of God.[20] They and the other Protestant groups applied the representative democratic organisation of their congregations also to the administration of their communities in wordly matters.[21][22] Rhode Island, Connecticut, and Pennsylvania added religious freedom to their democratic constitutions, becoming safe havens for persecuted religious minorities.[23][24][25] The first Bible printed in a European language in the Colonies was by German immigrant Christopher Sauer.[26] Nine of the thirteen colonies had official public religions. By the time of the Philadelphia Convention of 1787, the United States became one of the first countries in the world to codify freedom of religion into law, although this originally applied only to the federal government, and not to state governments or their political subdivisions.[要出典]
Modeling the provisions concerning religion within the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom, the framers of the United States Constitution rejected any religious test for office, and the First Amendment specifically denied the central government any power to enact any law respecting either an establishment of religion, or prohibiting its free exercise. In following decades, the animating spirit behind the constitution's Establishment Clause led to the disestablishment of the official religions within the member states. The framers were mainly influenced by secular, Enlightenment ideals, but they also considered the pragmatic concerns of minority religious groups who did not want to be under the power or influence of a state religion that did not represent them.[27] Thomas Jefferson, author of the Declaration of Independence said: "The priest has been hostile to liberty. He is always in alliance with the despot."[28]
Statistics
[編集]The following information is an estimation as actual statistics constantly vary. According to the CIA,[29] the following is the percentage of followers of different religions in the United States:
- Christian: (80.2%)
- Protestant (51.3%)
- Roman Catholic (23.9%)
- Mormon (1.7%)
- Other Christian (1.6%)
- Remainder of Christians (1.7%)
- Unaffiliated (12.1%)
- None (4%)
- Other/Unspecified (3%)
- Jewish (1.7%)
- Buddhist (0.7%)
- Muslim (0.6%)
Folklore
[編集]National holidays
[編集]




The United States observes holidays derived from events in American history, Christian traditions, and national patriarchs.
Thanksgiving is the principal traditionally American holiday. It evolved from the English Pilgrim's custom of giving thanks for one's welfare. Thanksgiving is generally celebrated as a family reunion with a large afternoon feast. Christmas Day, celebrating the birth of Jesus Christ, is widely celebrated and a federal holiday, though a fair amount of its current cultural importance is due to secular reasons. European colonization has led to some other Christian holidays such as Easter, Lent and St. Patrick’s Day to be observed, though with varying degrees of religious fidelity.
Independence Day (also known as the Fourth of July) celebrates the anniversary of the country’s Declaration of Independence from Great Britain. It is generally observed by parades throughout the day and the shooting of fireworks at night.
Halloween is thought to have evolved from the ancient Celtic/Gaelic festival of Samhain, which was introduced in the American colonies by Irish settlers. It has become a holiday that is celebrated by children and teens who traditionally dress up in costumes and go door to door trick-or-treating for candy. It also brings about an emphasis on eerie and frightening urban legends and movies.
Additionally, Mardi Gras, which evolved from the Catholic tradition of Carnival, is observed notably in New Orleans, St. Louis, and Mobile, Alabama as well as numerous other towns.
Federally recognized holidays are as follows:
| Date | Official Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year's Day | Celebrates beginning of the Gregorian calendar year. Festivities include counting down to midnight (12:00 am) on the preceding night, New Year's Eve. Traditional end of holiday season. |
| Third Monday in January | Birthday of Martin Luther King, Jr., or Martin Luther King, Jr. Day | Honors Martin Luther King, Jr., Civil Rights leader, who was actually born on January 15, 1929; combined with other holidays in several states. |
| First January 20 following a Presidential election | Inauguration Day | Observed only by federal government employees in Washington D.C., and the border counties of Maryland and Virginia to relieve traffic congestion that occurs with this major event. Swearing-in of President of the United States and Vice President of the United States. Celebrated every fourth year. Note: Takes place on January 21 if the 20th is a Sunday (although the President is still privately inaugurated on the 20th). If Inauguration Day falls on a Saturday or a Sunday, the preceding Friday or following Monday is not a Federal Holiday |
| Third Monday in February | Washington's Birthday | Washington's Birthday was first declared a federal holiday by an 1879 act of Congress. The Uniform Holidays Act, 1968, shifted the date of the commemoration of Washington's Birthday from February 22 to the third Monday in February. Many people now refer to this holiday as "Presidents' Day" and consider it a day honoring all American presidents. However, neither the Uniform Holidays Act nor any subsequent law changed the name of the holiday from Washington's Birthday to Presidents' Day.[30] |
| Last Monday in May | Memorial Day | Honors the nation's war dead from the Civil War onwards; marks the unofficial beginning of the summer season. (traditionally May 30, shifted by the Uniform Holidays Act 1968) |
| July 4 | Independence Day | Celebrates Declaration of Independence, also called the Fourth of July. |
| First Monday in September | Labor Day | Celebrates the achievements of workers and the labor movement; marks the unofficial end of the summer season. |
| Second Monday in October | Columbus Day | Honors Christopher Columbus, traditional discoverer of the Americas. In some areas it is also a celebration of Italian culture and heritage. (traditionally October 12); celebrated as American Indian Heritage Day and Fraternal Day in Alabama;[31] celebrated as Native American Day in South Dakota.[32] In Hawaii, it is celebrated as Discoverer's Day, though is not an official state holiday.[33] |
| November 11 | Veterans Day | Honors all veterans of the United States armed forces. A traditional observation is a moment of silence at 11:00 am remembering those killed in war. (Commemorates the 1918 armistice, which began at "the eleventh hour of the eleventh day of the eleventh month.") |
| Fourth Thursday in November | Thanksgiving Day | Traditionally celebrates the giving of thanks for the autumn harvest. Traditionally includes the consumption of a turkey dinner. Traditional start of the holiday season. |
| December 25 | Christmas | Celebrates the Nativity of Jesus. Some people [誰?] consider aspects of this religious holiday, such as giving gifts and decorating a Christmas tree, to be secular rather than explicitly Christian. |
- Federal Holidays Calendars from the federal Office of Personnel Management.
Fashion and dress
[編集]
Fashion in the United States is eclectic and predominantly informal. While Americans' diverse cultural roots are reflected in their clothing, particularly those of recent immigrants, cowboy hats and boots and leather motorcycle jackets are emblematic of specifically American styles.
Blue jeans were popularized as work clothes in the 1850s by merchant Levi Strauss, a German-Jewish immigrant in San Francisco, and adopted by many American teenagers a century later. They are worn in every state by people of all ages and social classes. Along with mass-marketed informal wear in general, blue jeans are arguably one of US culture's primary contributions to global fashion.[34]
Though informal dress is more common, certain professionals, such as bankers and lawyers, traditionally dress formally for work, and some occasions, such as weddings, funerals, dances, and some parties, typically call for formal wear.
Names
[編集]The United States has few laws governing given names. Traditionally, the right to name your child or yourself as you choose has been upheld by court rulings and is rooted in the Due Process Clause of the fourteenth Amendment of the United States Constitution and the Free Speech Clause of the First Amendment. A few restrictions do exist. Restrictions vary by state, but most are for the sake of practicality (for example: limiting the number of characters due to limitations in record keeping software). This freedom, along with the cultural diversity in the United States has given rise to a wide variety of names and naming trends. Creativity has also long been a part of American naming traditions and names have been used to express personality, cultural identity, and values[35][36] Naming trends vary by race, geographic area, and socioeconomic status. African Americans, for instance, have developed a very distinct naming culture.[36] Religious names are very common as well as names inspired by popular culture.[37]
Sports
[編集]

Baseball is the oldest of the major American team sports. Professional baseball dates from 1869 and had no close rivals in popularity until the 1960s. Though baseball is no longer the most popular sport,[38] it is still referred to as "the national sport". Also unlike the professional levels of the other popular spectator sports in the U.S., Major League Baseball teams play almost every day. The Major League Baseball regular season consists of each of the 30 teams playing 162 games from April to September. The season ends with the postseason and World Series in October.
American football, known in the United States as simply "football", now attracts more television viewers than any other sport and is considered to be the most popular sport in the United States.[39] The 32-team National Football League (NFL) is the most popular professional American football league. The National Football League differs from the other three major pro sports leagues in that each of its 32 teams plays one game a week over 17 weeks, for a total of 16 games with one bye week for each team. The NFL season lasts from September to December, ending with the playoffs and Super Bowl in January and February. Its championship game, the Super Bowl, has often been the highest rated television show, with an audience of over 100 million viewers annually.[要出典]
College football also attracts audiences of millions. Some communities, particularly in rural areas, place great emphasis on their local high school football team. American football games usually include cheerleaders and marching bands, which aim to raise school spirit and entertain the crowd at half-time.
Basketball is another major sport, represented professionally by the National Basketball Association. It was invented in Springfield, Massachusetts in 1891, by Canadian-born physical education teacher James Naismith. College basketball is also popular, due in large part to the NCAA men's Division I basketball tournament in March, also known as March Madness.
Ice hockey is the fourth leading professional team sport. Always a mainstay of Great Lakes and New England-area culture, the sport gained tenuous footholds in regions like the American South since the early 1990s, as the National Hockey League pursued a policy of expansion.[40]
Lacrosse is a team sport of American and Canadian Native American origin, it's the fastest growing sport in the United States.[41] Lacrosse is most popular in the East Coast area. NLL and MLL are the national box and outdoor lacrosse leagues, respectively, and have increased their following in recent years. Also, many of the top Division I college lacrosse teams draw upwards of 7–10,000 for a game, especially in the Mid-Atlantic and New England areas.
The sport called "football" in many countries is typically called soccer in the United States. A nineteen-team professional league, Major League Soccer, plays from March to October, but its television audience and overall popularity lag behind other American professional sports.[42] However, soccer is very popular as a participation sport, particularly among youths, and the US national soccer teams are competitive internationally.
Boxing and horse racing were once[いつ?] the most watched individual sports, but they have been eclipsed by golf and auto racing, particularly NASCAR.[要出典] Other popular sports are tennis, softball, rodeo, swimming, water polo, fencing, shooting sports, hunting, volleyball, skiing, snowboarding, skateboarding, cycling, MMA, wrestling, weightlifting and rugby.
The United States is unusually competitive in women's sports, a fact usually attributed to the Title IX antidiscrimination law, which requires most American colleges to give equal funding to men's and women's sports.[43] Despite that, however, women's sports are not nearly as popular among spectators as men's sports.
The United States enjoys a great deal of success both in the Summer Olympics and Winter Olympics, constantly being ranked in the top rankings.
Sports and community culture
[編集]Homecoming is an annual tradition of the United States. People, towns, high schools and colleges come together, usually in late September or early October, to welcome back former residents and alumni. It is built around a central event, such as a banquet, a parade, and most often, a game of American football, or, on occasion, basketball, wrestling or ice hockey. When celebrated by schools, the activities vary. However, they usually consist of a football game, played on the school's home football field, activities for students and alumni, a parade featuring the school's marching band and sports teams, and the coronation of a Homecoming Queen.
American high schools commonly field football, basketball, baseball, softball, volleyball, soccer, golf, swimming, track and field, and cross-country teams as well.
Cuisine
[編集]The cuisine of the United States is extremely diverse, owing to the vastness of the continent, the relatively large population (1/3 of a billion people) and the number of native and immigrant influences. Mainstream American culinary arts are similar to those in other Western countries. Wheat and corn are the primary cereal grains. Traditional American cuisine uses ingredients such as turkey, white-tailed deer venison, potatoes, sweet potatoes, corn, squash, and maple syrup, indigenous foods employed by American Indians and early European settlers.
The types of food served at home vary greatly and depend upon the region of the country and the family's own cultural heritage. Recent immigrants tend to eat food similar to that of their country of origin, and Americanized versions of these cultural foods, such as American Chinese cuisine, Tex-Mex (Mexican-American cuisine) or Italian-American cuisine often eventually appear; an example is Vietnamese cuisine, Korean cuisine and Thai cuisine. German cuisine has a profound impact on American cuisine, especially mid-western cuisine, with potatoes, noodles, roasts, stews and cakes/pastries being the most iconic ingredients in both cuisines.[7] Dishes such as the hamburger, pot roast, baked ham and hot dogs are examples of American dishes derived from German cuisine.[44][45]
Different regions of the United States have their own cuisine and styles of cooking. The state of Louisiana, for example, is known for its Cajun and Creole cooking. Cajun and Creole cooking are influenced by French, Acadian, and Haitian cooking, although the dishes themselves are original and unique. Examples include Crawfish Etouffee, Red Beans and Rice, Seafood or Chicken Gumbo, Jambalaya, and Boudin. Italian, German, Hungarian and Chinese influences, traditional Native American, Caribbean, Mexican and Greek dishes have also diffused into the general American repertoire. It is not uncommon for a "middle-class" family from "middle America" to eat, for example, restaurant pizza, home-made pizza, enchiladas con carne, chicken paprikas, beef stroganof and bratwurst with sauerkraut for dinner throughout a single week.
Soul food, developed by African slaves, is popular around the South and among many African Americans elsewhere. Syncretic cuisines such as Louisiana creole, Cajun, Pennsylvania Dutch, and Tex-Mex are regionally important. Iconic American dishes such as apple pie, fried chicken, pizza, hamburgers, and hot dogs derive from the recipes of various immigrants and domestic innovations. French fries, Mexican dishes such as burritos and tacos, and pasta dishes freely adapted from Italian sources are consumed.[46]
Americans generally prefer coffee to tea, with more than half the adult population drinking at least one cup a day.[47] Marketing by U.S. industries is largely responsible for making orange juice and milk (now often fat-reduced) ubiquitous breakfast beverages.[48] During the 1980s and 1990s, Americans' caloric intake rose 24%;[46] frequent dining at fast food outlets is associated with what health officials call the American "obesity epidemic." Highly sweetened soft drinks are popular; sugared beverages account for 9% of the average American's daily caloric intake.[49]
Hamburgers and fries, as well as doughnuts are considered American foods.[50][51]
Some representative American foods
-
Traditional Thanksgiving dinner with turkey, dressing, sweet potatoes, and cranberry sauce.
-
A cream-based New England chowder, traditionally made with clams and potatoes.
-
A Caesar salad containing croutons, Parmesan cheese, lemon juice, olive oil, Worcestershire, and pepper.
-
Creole Jambalaya with shrimp, ham, tomato, and Andouille sausage.
-
Chicken Fried Steak (alternatively known as Country Fried Steak)
-
California club pizza with avocados and tomatoes.
-
A submarine sandwich, which includes a variety of Italian luncheon meats.
-
American style breakfast with pancakes, maple syrup, sausage links, bacon strips, and fried eggs.
-
A hot dog sausage topped with beef chili, white onions and mustard.
-
A meatloaf with a tomato sauce topping.
-
An apple cobbler dessert.
Family structure
[編集]
Family arrangements in the United States reflect the nature of contemporary American society, as they always have. Although the nuclear family concept (two-married adults with biological children) holds a special place in the mindset of Americans, it is single-parent families, childless/childfree couples, and fused families which now constitute the majority of families.[要出典] A person may grow up in a single-parent family, go on to marry and live in childless couple arrangement, then get divorced, live as a single for a couple of years, re-marry, have children and live in a nuclear family arrangement.[1][52]
"The nuclear family... is the idealized version of what most people think when they think of "family..." The old definition of what a family is... the nuclear family- no longer seems adequate to cover the wide diversity of household arrangements we see today, according to many social scientists (Edwards 1991; Stacey 1996). Thus has arisen the term postmodern family, which is meant to describe the great variability in family forms, including single-parent families and child-free couples."- Brian K. Williams, Stacey C. Sawyer, Carl M. Wahlstrom, Marriages, Families & Intinamte Relationships, 2005.[52]
| Year | Families (69.7%) | Non-families (31.2%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Married couples (52.5%) | Single Parents | Other blood relatives | Singles (25.5%) | Other non-family | |||
| Nuclear family | Without children | Male | Female | ||||
| 2000 | 24.1% | 28.7% | 9.9% | 7% | 10.7% | 14.8% | 5.7% |
| 1970 | 40.3% | 30.3% | 5.2% | 5.5% | 5.6% | 11.5% | 1.7% |
Single-parent households are households consisting of a single adult (most often a woman) and one or more children. In the single-parent household, one parent typically raises the children with little to no help from the other. This parent is the sole "breadwinner" of the family and thus these households are particularly vulnerable economically. They have higher rates of poverty, and children of these households are more likely to have educational problems.[要出典]
Youth Dependence
[編集]Other changes to the landscape of American family arrangements include dual-income earner households and delayed independence among American youths. Whereas most families in the 1950s and 1960s relied on one income earner, most commonly the husband, the vast majority of family households now have two-income earners.[要出典][要説明]
Another change is the increasing age at which young Americans leave their parental home. Traditionally, a person past "college age" who lived with their parent(s) was viewed negatively, but today it is not uncommon for children to live with their parents until their mid-twenties. This trend can be mostly attributed to rising living costs that far exceed those in decades past. Thus, many young adults now remain with their parents well past their mid-20s. This topic was a cover article of TIME magazine in 2005.[要出典]
Exceptions to the custom of leaving home in one's mid-20s can occur especially among Italian and Hispanic Americans, and in expensive urban real estate markets such as New York City,[53] California,[54] and Honolulu,[55] where monthly rents commonly exceed $1000 a month.
Housing
[編集]Historically, Americans mainly lived rural lives, with a few important cities of moderate size. Following World War II, however, Americans began living in increasing numbers in the suburbs, belts around major cities with higher density than rural areas, but much lower than urban areas. This move has been attributed to many factors such as the automobile, the availability of large tracts of land, the convenience of more and longer paved roads, increasing violence in urban centers (see white flight), and the lower expense of housing.[要出典]
These new single-family houses were usually one or two stories tall, and often were part of large contracts of homes built by a single developer and often with little variation (sometimes referred to as cookie cutter houses or homes). Houses were separated. The resulting low-density development was given the pejorative label urban sprawl.[要出典]
This has changed;en:Template:how[いつ?] white flight has reversed, with Yuppies and upper-middle-class, empty nest Baby Boomers returning to urban living, usually in condominia, such as in New York City's Lower East Side, Chicago's South Loop and Miami's Brickell Neighborhood. The result has been the displacement of many poorer, inner-city residents.[要出典]
American cities with housing prices near the national median have also been losing the middle income neighborhoods, those with median income between 80% and 120% of the metropolitan area's median household income. Here, the more affluent members of the middle class, who are also often referred to as being professional or upper middle class, have left in search of larger homes in more exclusive suburbs. This trend is largely attributed to the Middle-class squeeze, which has caused a starker distinction between the statistical middle class and the more privileged members of the middle class.[56] In more expensive areas such as California, however, another trend has been taking place where an influx of more affluent middle-class households has displaced those in the actual middle of society and converted former middle-middle-class neighborhoods into upper-middle-class neighborhoods.[57]

The population of rural areas has been declining over time as more and more people migrate to cities for work and entertainment. The great exodus from the farms came in the 1940s; in recent years fewer than 2% of the population lives on farms (though others live in the countryside and commute to work). Electricity and telephone, and sometimes cable and Internet services are available to all but the most remote regions.
About half of Americans now live in what is known as the suburbs. The suburban nuclear family has been identified as part of the "American Dream": a married couple with children owning a house in the suburbs. This archetype is reinforced by mass media, religious practices, and government policies and is based on traditions from Anglo-Saxon cultures. One of the biggest differences in suburban living as compared to urban living is the housing occupied by the families. The suburbs are filled with single-family homes separated from retail districts, industrial areas, and sometimes even public schools. However, many American suburbs are incorporating these districts on smaller scales, attracting more people to these communities.[要出典]
Housing in urban areas may include more apartments and semi-attached homes than in the suburbs or small towns. Aside from housing, the major difference from suburban living is the density and diversity of many different subcultures, as well as retail and manufacturing buildings mixed with housing in urban areas.[要出典]
Automobiles and commuting
[編集]Due to the low overall population density as well as urban sprawl, the United States is one of the few developed nations where most people commute by car.
The rise of suburbs and the need for workers to commute to cities brought about the popularization of automobiles. In 2001, 90% of Americans drove to work in cars.[58] Lower energy and land costs favor the production of relatively large, powerful cars. The culture in the 1950s and 1960s often catered to the automobile with motels and drive-in restaurants. Outside of relatively few urban areas, it is considered a necessity for most Americans to own and drive cars. New York City is the only locality in the United States where more than half of all households do not own a car.[58]
Social class and work
[編集]Though most Americans in the 21st century identify themselves as middle class, American society and its culture are considerably fragmented.[1][59][60] Social class, generally described as a combination of educational attainment, income and occupational prestige, is one of the greatest cultural influences in America.[1] Nearly all cultural aspects of mundane interactions and consumer behavior in the U.S. are guided by a person's location within the country's social structure.
Distinct lifestyles, consumption patterns and values are associated with different classes. Early sociologist-economist Thorstein Veblen, for example, noted that those at the very top of the social ladder engage in conspicuous leisure as well as conspicuous consumption. Upper-middle-class persons commonly identify education and being cultured as prime values. Persons in this particular social class tend to speak in a more direct manner that projects authority, knowledge and thus credibility. They often tend to engage in the consumption of so-called mass luxuries, such as designer label clothing. A strong preference for natural materials and organic foods as well as a strong health consciousness tend to be prominent features of the upper middle class. American middle-class individuals in general value expanding one's horizon, partially because they are more educated and can afford greater leisure and travels. Working-class individuals take great pride in doing what they consider to be "real work," and keep very close-knit kin networks that serve as a safeguard against frequent economic instability.[1][61][62]

Working-class Americans as well as many of those in the middle class may also face occupation alienation. In contrast to upper-middle-class professionals who are mostly hired to conceptualize, supervise and share their thoughts, many Americans have little autonomy or creative latitude in the workplace.[64] As a result white collar professionals tend to be significantly more satisfied with their work.[65][66] More recently those in the center of the income strata, who may still identify as middle class, have faced increasing economic insecurity,[67] supporting the idea of a working-class majority.[68]
Political behavior is affected by class; more affluent individuals are more likely to vote, and education and income affect whether individuals tend to vote for the Democratic or Republican party. Income also had a significant impact on health as those with higher incomes had better access to health care facilities, higher life expectancy, lower infant mortality rate and increased health consciousness.[要出典] This is particularly noticeable with black voters who are often socially conservative, yet overwhelmingly vote Democratic.[69][70]
In the United States occupation is one of the prime factors of social class and is closely linked to an individual’s identity. The average work week in the U.S. for those employed full-time was 42.9 hours long with 30% of the population working more than 40 hours a week.[71] The Average American worker earned $16.64 an hour in the first two quarters of 2006.[72] Overall Americans worked more than their counterparts in other developed post-industrial nations. While the average worker in Denmark enjoyed 30 days of vacation annually, the average American had 16 annual vacation days.[73]
In 2000 the average American worked 1,978 hours per year, 500 hours more than the average German, yet 100 hours less than the average Czech. Overall the U.S. labor force is one of the most productive in the world, largely due to its workers working more than those in any other post-industrial country (excluding South Korea).[63] Americans generally hold working and being productive in high regard; being busy and working extensively may also serve as the means to obtain esteem.[62]
Race and ancestry
[編集]| このページは更新が必要とされています。 このページには古い情報が掲載されています。編集の際に新しい情報を記事に反映させてください。反映後、このタグは除去してください。(2013年8月) |
Race in the United States is based on physical characteristics and skin color and has played an essential part in shaping American society even before the nation's conception.[1] Until the civil rights movement of the 1960s, racial minorities in the United States faced institutionalized discrimination and social as well as economic marginalization.[74] Today the U.S. Department of Commerce's Bureau of the Census recognizes four races, Native American or American Indian, African American, Asian and White (European American). According to the U.S. government, Hispanic Americans do not constitute a race, but rather an ethnic group. During the 2000 U.S. Census Whites made up 75.1% of the population with those being Hispanic or Latino constituting the nation's prevalent minority with 12.5% of the population. African Americans made up 12.3% of the total population, 3.6% were Asian American and 0.7% were Native American.[75]
The Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution—ratified on Dec 6, 1865—abolished slavery in the United States. The northern states had outlawed slavery in their territory in the late 18th and early 19th century, though their industrial economies relied on raw materials produced by slaves. Following the Reconstruction period in the 1870s, an apartheid regulation emerged in the Southern states named the Jim Crow laws that provided for legal segregation. Lynching was practiced throughout the U.S., including in the Northern states, until the 1930s, while continuing well into the civil rights movement in the South.[74]
Chinese Americans were earlier marginalized as well during a significant proportion of U.S. history. Between 1882 and 1943 the United States instituted the Chinese Exclusion Act barring Chinese immigrants from entering the U.S. During the second world war roughly 120,000 Japanese Americans, 62% of whom were U.S. citizens,[76] were imprisoned in Japanese internment camps by the U.S. government following the attacks on Pearl Harbor, an American Military Base, by Japanese troops.
Due to exclusion from or marginalization by earlier mainstream society, there emerged a unique sub-culture among the racial minorities in the United States. During the 1920s, Harlem, New York became home to the Harlem Renaissance. Music styles such as Jazz, Blues, Rap, Rock and roll as well as numerous folk-songs such as Blue Tail Fly (Jimmy Crack Corn) originated within the realms of African American culture, and was later on adopted by the mainstream.[74] Chinatowns can be found in many cities across the country and Asian cuisine has become a common staple in mainstream America. The Hispanic community has also had a dramatic impact on American culture. Today, Catholics are the largest religious denomination in the United States and out-number Protestants in the South-west and California.[77] Mariachi music and Mexican cuisine are commonly found throughout the Southwest, with some Latin dishes, such as burritos and tacos, found anywhere in the nation.
Economic variance and substantive segregation, is commonplace in the United States. Asian Americans have median household income and educational attainment exceeding that of other races. African Americans, Hispanics and Native Americans have considerably lower income and education than do White Americans or Asian Americans.[78][79] In 2005 the median household income of Whites was 62.5% higher than that of African American, nearly one-quarter of whom live below the poverty line.[78] 46.9% of homicide victims in the United States are African American.[74][80]
After the attacks by Muslim terrorists on September 11, 2001, discrimination against Arabs and Muslims in the U.S. rose significantly. The American-Arab Anti-Discrimination Committee (ADC) reported an increase in hate speech, cases of airline discrimination, hate crimes, police misconduct as well as racial profiling.[81]
Death and funerals
[編集]
It is customary for Americans to hold a wake in a funeral home within a couple days of the death of a loved one. The body of the deceased may be embalmed and dressed in fine clothing if there will be an open-casket viewing. Traditional Jewish and Muslim practice include a ritual bath and no embalming. Friends, relatives and acquaintances gather, often from distant parts of the country, to "pay their last respects" to the deceased. Flowers are brought to the coffin and sometimes eulogies, elegies, personal anecdotes or group prayers are recited. Otherwise, the attendees sit, stand or kneel in quiet contemplation or prayer. Kissing the corpse on the forehead is typical among Italian Americans[82] and others. Condolences are also offered to the widow or widower and other close relatives.
A funeral may be held immediately afterwards or the next day. The funeral ceremony varies according to religion and culture. American Catholics typically hold a funeral mass in a church, which sometimes takes the form of a Requiem mass. Jewish Americans may hold a service in a synagogue or temple. Pallbearers carry the coffin of the deceased to the hearse, which then proceeds in a procession to the place of final repose, usually a cemetery. The unique Jazz funeral of New Orleans features joyous and raucous music and dancing during the procession.
Mount Auburn Cemetery (founded in 1831) is known as "America's first garden cemetery."[83] American cemeteries created since are distinctive for their park-like setting. Rows of graves are covered by lawns and are interspersed with trees and flowers. Headstones, mausoleums, statuary or simple plaques typically mark off the individual graves. Cremation is another common practice in the United States, though it is frowned upon by various religions. The ashes of the deceased are usually placed in an urn, which may be kept in a private house, or they are interred. Sometimes the ashes are released into the atmosphere. The "sprinkling" or "scattering" of the ashes may be part of an informal ceremony, often taking place at a scenic natural feature (a cliff, lake or mountain) that was favored by the deceased.
A so-called death industry has developed in the United States that has replaced earlier, more informal traditions. Before the popularity of funeral homes, people usually held wakes in the Parlour rooms of private houses.[要出典]
Sociological issues
[編集]Marriage and divorce
[編集]Marriage laws are established by individual states. The typical wedding involves a couple proclaiming their commitment to one another in front of their close relatives and friends, often presided over by a religious figure such as a minister, priest, or rabbi, depending upon the faith of the couple. In traditional Christian ceremonies, the bride's father will "give away" (hand off) the bride to the groom. Secular weddings are also common, often presided over by a judge, Justice of the Peace, or other municipal official. Same-sex marriage is currently legal in several states; others offer domestic partnerships. Polygamy is universally banned.
Divorce is the province of state governments, so divorce law varies from state to state. Prior to the 1970s, divorcing spouses had to allege that the other spouse was guilty of a crime or sin like abandonment or adultery; when spouses simply could not get along, lawyers were forced to manufacture "uncontested" divorces. The no-fault divorce revolution began in 1969 in California; New York and South Dakota were the last states to begin allowing no-fault divorce. No-fault divorce on the grounds of "irreconcilable differences" is now available in all states. However, many states have recently required separation periods prior to a formal divorce decree.
State law provides for child support where children are involved, and sometimes for alimony. "Married adults now divorce two-and-a-half times as often as adults did 20 years ago and four times as often as they did 50 years ago... between 40% and 60% of new marriages will eventually end in divorce. The probability within... the first five years is 20%, and the probability of its ending within the first 10 years is 33%... Perhaps 25% of children ages 16 and under live with a stepparent."[84] The median length for a marriage in the U.S. today is 11 years with 90% of all divorces being settled out of court.
Race relations
[編集]White Americans (non-Hispanic/Latino and Hispanic/Latino) are the racial majority, with a 72% share of the U.S. population, according to the 2010 US Census.[85] Hispanic and Latino Americans comprise 15% of the population, making up the largest ethnic minority.[86] Black Americans are the largest racial minority, comprising nearly 13% of the population.[85][87] The White, non-Hispanic or Latino population comprises 63% of the nation's total.[86]
Throughout most of the country's history following independence from Great Britain, the majority race in the United States has been Caucasian, and the largest racial minority has been African-Americans. This relationship has historically been the most important one since the founding of the United States. Currently, most African-Americans are descendants of African slaves imported to the United States, though some are more recent immigrants or their descendants. Slavery existed in the United States at the time of the country's formation in the 1770s. The U.S. banned importation of slaves in 1808. Slavery was partially abolished by the Emancipation Proclamation issued by president Abraham Lincoln in 1862 for slaves in the Southeastern United States during the Civil War. Slavery was rendered illegal by the passage of the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. Jim Crow Laws prevented full use of African American citizenship until the 20th century. The Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s and the Civil Rights Act of 1964 outlawed official or legal segregation in public places or limited access to minorities.
Relations between white Americans and other racial or ethnic groups have been a source of tension at various times in U.S. history. With the advent of European colonization, and continuing into the early years of the republic, relations between whites and Native American was a significant issue. In 1882, in response to Chinese immigration due to the Gold Rush and the labor needed for the Transcontinental Railroad, the U.S. signed into law the Chinese Exclusion Act which banned immigration by Chinese people into the U.S. In the late 20th century, the growth of the Hispanic population in the U.S., fueled largely by Mexican immigration, generated debate over policies such as English as the official language and reform to immigration policies.
A huge majority of Americans of all races disapprove of racism. Nevertheless, some Americans continue to hold negative racial/ethnic stereotypes about various racial and ethnic groups. Professor Imani Perry, of Princeton University, has argued that contemporary racism in the United States "is frequently unintentional or unacknowledged on the part of the actor”,[88] believing that racism mostly stems unconsciously from below the level of cognition.[89]
Drugs and alcohol
[編集]en:Template:Refimprove section en:Template:Further

American attitudes towards drugs and alcoholic beverages have evolved considerably throughout the country's history. In the 19th century, alcohol was readily available and consumed, and no laws restricted the use of other drugs. Attitudes on drug addiction started to change, resulting in the Harrison Act, which eventually became proscriptive.
A movement to ban alcoholic beverages, called the Temperance movement, emerged in the late 19th century. Several American Protestant religious groups, as well as women's groups such as the Women's Christian Temperance Union, supported the movement. In 1919, Prohibitionists succeeded in amending the Constitution to prohibit the sale of alcohol. Although the Prohibition period did result in lowering alcohol consumption overall,[要出典] banning alcohol outright proved to be unworkable, as the previously legitimate distillery industry was replaced by criminal gangs that trafficked in alcohol. Prohibition was repealed in 1933. States and localities retained the right to remain "dry", and to this day, a handful still do.
During the Vietnam War era, attitudes swung well away from prohibition. Commentators noted that an 18-year-old could be drafted to war but could not buy a beer.
Since 1980, the trend has been toward greater restrictions on alcohol and drug use. The focus this time, however, has been to criminalize behaviors associated with alcohol, rather than attempt to prohibit consumption outright. New York was the first state to enact tough drunk-driving laws in 1980; since then all other states have followed suit. All states have also banned the purchase of alcoholic beverages by individuals under 21.
A "Just Say No to Drugs" movement replaced the more liberal ethos of the 1960s. This led to stricter drug laws and greater police latitude in drug cases. Drugs are, however, widely available, and 16% of Americans 12 and older used an illicit drug in 2012.[90]
Since the 1990s, marijuana use has become increasingly tolerated in America, with a number of states allowing the use of marijuana for medical purposes. In most states marijuana is still illegal without medical prescription. In the 2012 general election, voters in the states of Colorado and Washington approved the legalization of marijuana for recreational use. Marijuana is classified as illegal under federal law.
Group affiliations
[編集]As the United States is a diverse nation, there are numerous organizations and social groups, and individuals may derive their group affiliated identity from a variety of sources. Many Americans, especially white collar professionals belong to professional organizations such as the APA, ASA or ATFLC, although books like Bowling Alone indicate that Americans affiliate with these sorts of groups less often than they did in the 1950s and 1960s. Today, Americans derive a great deal of their identity through their work and professional affiliation, especially among individuals higher on the economic ladder. Recently professional identification has led to many clerical and low-level employees giving their occupations new, more respectable titles, such as "Sanitation service engineer" instead of "Janitor."[1]
Additionally many Americans belong to non-profit organizations and religious establishments and may volunteer their services to such organizations. Rotary International, the Knights of Columbus or even the Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals are examples of such non-profit and mostly volunteer-run organizations. Ethnicity plays another important role in providing some Americans with group identity,[74] especially among those who recently immigrated.[91]
Many American cities are home to ethnic enclaves such as a Chinatown and Little Italies. Local patriotism may be also provide group identity. For example, a person may be particularly proud to be from California or New York City, and may display clothing from local sports team.
Political lobbies such as the AARP, ADL, NAACP, NOW and GLAAD (examples being civil rights activist organizations) not only provide individuals with a sentiment of intra-group allegiance but also increase their political representation in the nation's political system. Combined, profession, ethnicity, religious, and other group affiliations have provided Americans with a multitude of options to derive group based identity from.[1]
Volunteerism
[編集]De Tocqueville first noted, in 1835, the American attitude towards helping others in need. A 2011 Charities Aid Foundation study found that Americans were the first most willing to help a stranger and donate time and money in the world at 60%. Many low-level crimes are punished by assigning hours of "community service", a requirement that the offender perform volunteer work;[92] some high schools also require community service to graduate. Since US citizens are required to attend jury duty, they can be jurors in legal proceedings.
Military culture
[編集]From the time of its inception the military played a decisive role in the history of the United States. A sense of national unity and identity was forged out of the victorious First Barbary War and Second Barbary War, as well as the War of 1812. Even so, the Founders were suspicious of a permanent military force and not until the outbreak of World War II did a large standing army become officially established. The National Security Act of 1947, adopted following World War II and during the onset of the Cold War, created the modern U.S. military framework; the Act merged previously Cabinet-level Department of War and the Department of the Navy into the National Military Establishment (renamed the Department of Defense in 1949), headed by the Secretary of Defense; and created the Department of the Air Force and National Security Council.
The U.S. military is one of the largest militaries in terms of number of personnel. It draws its manpower from a large pool of paid volunteers; although conscription has been used in the past in various times of both war and peace, it has not been used since 1972. As of 2011, the United States spends about $550 billion annually to fund its military forces,[93] and appropriates approximately $160 billion to fund Overseas Contingency Operations. Put together, the United States constitutes roughly 43 percent of the world's military expenditures. The U.S. armed forces as a whole possess large quantities of advanced and powerful equipment, along with widespread placement of forces around the world, giving them significant capabilities in both defense and power projection.
There is and has been a strong military culture among those on active duty, those not on active duty, as well as veterans.
Gun culture
[編集]
In sharp contrast to most other developed nations, firearms laws in the United States are permissive and private gun ownership is common, with just under half of American households containing at least one firearm.[94] In fact, there are more privately owned firearms in the United States than in any other country, both per capita and in total.[95] Rates of gun ownership vary significantly by region and by state, with gun ownership most common in Alaska, the Frontier Strip, the Mountain States and the South, and least prevalent in Hawaii, the island territories, California, the Northeast megalopolis. Gun ownership tends to be more common in rural than in urban areas.[96]
Hunting, plinking and target shooting are popular pastimes, although ownership of firearms for purely utilitarian purposes such as personal protection is common as well. In fact, personal protection was the most common reason given for gun ownership in a 2013 Gallup poll of gun owners, at 60%.[97] Ownership of handguns, while not uncommon, is less common than ownership of long guns. Gun ownership is considerably more prevalent among men than among women, with men being approximately four times more likely than women to report owning guns.[98]
Other aspects
[編集]In the federal government of the United States, responsibilities that are usually in a cultural minister's portfolio elsewhere are divided among the Federal Communications Commission, the Corporation for Public Broadcasting, the U.S. Department of Commerce, the U.S. Department of the Interior, the U.S. Department of State, the National Endowment for the Humanities, the National Endowment for the Arts, the U.S. Commission of Fine Arts, the Library of Congress, the Smithsonian Institution, and the National Gallery of Art. However, many state and city governments have a department dedicated to cultural affairs.
Influence
[編集]The Hollywood cinema industry has been very influential on American culture, and to some extent in global culture through transmission of American movies overseas and as other film cultures like Bollywood have striven to emulate the American model.
The United States has influenced the cultures of many other countries, but as countries around the world become more inter-connected and inter-dependent, the general cultural trends (of the US and other countries) head towards multiculturalism and sociocultural globalization.
関連項目
[編集]- Americana
- American studies
- 1950s' American automobile culture
- Body contact and personal space in the United States
- Culture of the Southern United States
- Folklore of the United States
- Etiquette in North America
- Philanthropy in the United States
- Protestant work ethic
- Work and Travel USA (organization)
- America 24/7 (book)
- Stereotypes of Americans
参考文献
[編集]- ^ a b c d e f g h i Thompson, William; Joseph Hickey (2005). Society in Focus. Boston, MA: Pearson. ISBN 0-205-41365-X 引用エラー: 無効な
<ref>タグ; name "Society in Focus"が異なる内容で複数回定義されています - ^ Kirschbaum, Erik (1986). The eradication of German culture in the United States, 1917-1918. H.-D. Heinz. p. 155. ISBN 3-88099-617-2
- ^ a b "Mr. Jefferson and the giant moose: natural history in early America", Lee Alan Dugatkin. University of Chicago Press, 2009. ISBN 0-226-16914-6, ISBN 978-0-226-16914-9. University of Chicago Press, 2009. Chapter x.
- ^ McDonald, James (2010) Interplay:Communication, Memory, and Media in the United States. Goettingen: Cuvillier, p. 120. ISBN 3-86955-322-7.
- ^ http://www.hoover.org/publications/hoover-digest/article/132541
- ^ Clack, George, et al. (September 1997). “Chapter 1”. One from Many, Portrait of the USA. United States Information Agency
- ^ a b Adams, J.Q.; Pearlie Strother-Adams (2001). Dealing with Diversity. Chicago, IL: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. ISBN 0-7872-8145-X
- ^ “American Religious Identification Survey”. www.gc.cuny.edu. 2010年1月1日閲覧。[リンク切れ]
- ^ Hine, Darlene; William C. Hine; Stanley Harrold (2006). The African American Odyssey. Boston, MA: Pearson
- ^ 1989 book, Albion's Seed (ISBN 0195069056), Paul Berinde
- ^ 2011, American Nations, ISBN 978-0143122029, Penguin Books
- ^ “Selected Social Characteristics in the United States: 2007”. United States Census Bureau. 2008年10月9日閲覧。
- ^ United States, CIA World Facebook.
- ^ "Famous American Trials: John Peter Zenger Trial 1735", Doug Linder. University of Missouri-Kansas City. 2001. Accessed September 9, 2010.
- ^ "American history told by contemporaries..., Volume 2", John Gould Curtis. The Macmillan company, 1919. p. 192.
- ^ Meyers, Jeffrey (1999). Hemingway: A Biography. New York: Da Capo, p. 139. ISBN 0-306-80890-0.
- ^ Dell Upton. 1998. "Architecture in the United States-Oxford history of art." pp. 11 ff. ISBN 0-19-284217-X
- ^ “U.S. Stands Alone in its Embrace of Religion”. Pew Global Attitudes Project. January 1, 2007閲覧。
- ^ O'Hehir, Andrew (20 January 2013). “Why do we care if Lance apologizes?”. Salon. Salon Media Group. 20 January 2013閲覧。
- ^ M. Schmidt, Pilgerväter, in Die Religion in Geschichte und Gegenwart, 3. Auflage, Band V, Tübingen (Germany), col. 384
- ^ Allan Weinstein and David Rubel (2002), The Story of America: Freedom and Crisis from Settlement to Superpower, DK Publishing, New York, N.Y., p. 61
- ^ Clifton E. Olmstead (1960), History of Religion in the United States, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., pp. 63-65
- ^ Clifton E.Olmstead, History of Religion, pp. 74-75, 99, 104-105, 114-115
- ^ Hans Fantel (1974), William Penn: Apostle of Dissent, William Morrow and Co., New York, N.Y.
- ^ Edwin S. Gaustad (1999), Liberty of Conscience: Roger Williams in America, Judson Press, Valley Forge
- ^ "1795–1895. One hundred years of American commerce", Chauncey Mitchell Depew. D.O. Haynes, 1895. p. 309.
- ^ Marsden, George M. 1990. Religion and American Culture. Orlando: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, pp.45–46.
- ^ Jefferson, Thomas (1904). The writings of Thomas Jefferson. Thomas Jefferson Memorial Association of the United States. p. 119
- ^ “CIA Fact Book”. CIA World Fact Book (2002年). 2007年12月30日閲覧。
- ^ “5 USC § 6103 - Holidays | LII / Legal Information Institute”. .law.cornell.edu. 2012年6月3日閲覧。
- ^ “Section 1-3-8”. Template:Cite webの呼び出しエラー:引数 accessdate は必須です。
- ^ “Holidays Observed”. South Dakota Public Utilities Commission. 14 August 2007時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。 Template:Cite webの呼び出しエラー:引数 accessdate は必須です。
- ^ “State agencies remain open for Discoverers Day”. The Honolulu Advertiser (2007年10月8日). 2012年6月3日閲覧。
- ^ Davis Fred (1992). Fashion, Culture, and Identity
- ^ Larson, Carlton F.W. (November 2011). “Naming Baby: The Constitutional Dimensions of Naming Rights”. George Washington Law Review 80 (1).
- ^ a b Wattenberg, Laura (May 7, 2013). The Baby Name Wizard, Revised 3rd Edition: A Magical Method for Finding the Perfect Name for Your Baby. Harmony. ISBN 0770436471
- ^ Rosenkrantz, Linda (August 29, 2006). Beyond Jennifer & Jason, Madison & Montana: What to Name Your Baby Now. Mass Market Paperback. ISBN 0312940955
- ^ “Poll: Adults who follow at least one sport”. Harris Interactive. Template:Cite webの呼び出しエラー:引数 accessdate は必須です。
- ^ Krane, David K. (2002年10月30日). “Professional Football Widens Its Lead Over Baseball as Nation's Favorite Sport”. Harris Interactive. September 14, 2007閲覧。 Maccambridge, Michael (2004). America's Game: The Epic Story of How Pro Football Captured a Nation. New York: Random House. ISBN 0-375-50454-0.
- ^ “Raw Numbers: The NHL’s Impact on the South”. The United States of Hockey (2011年5月19日). 2012年6月5日閲覧。
- ^ “Eight Interesting Facts About Team Sports Participation In America”. Template:Cite webの呼び出しエラー:引数 accessdate は必須です。
- ^ “Soccer will never be America's sport”. USA Today
- ^ “Amid 40th anniversary of Title IX, women set new standard in London”. CNN. (August 12, 2012)
- ^ “History of the hot dog”. 2006年10月18日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2006年11月13日閲覧。
- ^ “History of the Hamburger”. 2006年11月13日閲覧。
- ^ a b Klapthor, James N. (2003年8月23日). “What, When, and Where Americans Eat in 2003”. Institute of Food Technologists. 2007年6月19日閲覧。
- ^ “Coffee Today”. Coffee Country. PBS (May 2003). 2007年6月19日閲覧。
- ^ Smith, Andrew F. (2004). The Oxford Encyclopedia of Food and Drink in America. New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 131–32. ISBN 0-19-515437-1. Levenstein, Harvey (2003). Revolution at the Table: The Transformation of the American Diet. Berkeley, Los Angeles, and London: University of California Press, pp. 154–55. ISBN 0-520-23439-1. Pirovano, Tom (2007年). “Health & Wellness Trends—The Speculation Is Over”. AC Nielsen. 7 August 2007時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2007年6月12日閲覧。
- ^ “Fast Food, Central Nervous System Insulin Resistance, and Obesity”. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. American Heart Association (2005年). 2007年6月9日閲覧。 “Let's Eat Out: Americans Weigh Taste, Convenience, and Nutrition” (PDF). U.S. Dept. of Agriculture. 2007年6月9日閲覧。
- ^ The CHOW Editorial Team (19 June 2008). “The Hamburger Through Time”. CBS INTERACTIVE INC.. 16 April 2012閲覧。
- ^ Glazed America: Anthropologist Examines Doughnut as Symbol of Consumer Culture Newswise, Retrieved on July 22, 2008.
- ^ a b c Williams, Brian; Stacey C. Sawyer; Carl M. Wahlstrom (2005). Marriages, Families & Intimate Relationships. Boston, MA: Pearson. ISBN 0-205-36674-0
- ^ New York apartments pricing and New York NY apartment reviews Apartment Ratings
- ^ San Francisco apartments pricing and San Francisco CA apartment reviews Apartment Ratings
- ^ “Honolulu apartments pricing and Honolulu HI apartment reviews”. Apartmentratings.com. 2012年6月3日閲覧。
- ^ Harden, Blaine (2006年6月22日). “Washington Post, America is losing its middle income neighborhoods”. The Washington Post 2006年7月25日閲覧。
- ^ Harden, Blaine (2006年6月22日). “Washington Post, America is losing its middle income neighborhoods.”. The Washington Post 2006年7月25日閲覧。
- ^ a b Highlights of the 2001 National Household Travel Survey, Bureau of Transportation Statistics, U.S. Department of Transportation, accessed May 21, 2006
- ^ “Middle class according to The Drum Major Institute for public policy”. 2006年7月25日閲覧。
- ^ Fussel, Paul (1983). Class: A Guide through the American Status System. New York, NY: Touchstone. ISBN 0-671-79225-3
- ^ Fussel, Paul (1983). Class, A Guide through the American status system. New York, NY: Touchstone. ISBN 0-671-79225-3
- ^ a b Ehrenreich, Barbara (1989). Fear of Falling: The Inner Life of the Middle Class. New York, NY: HarperCollins. ISBN 0-06-097333-1
- ^ a b “CNN, work in American, UN report finds Americans most productive, 2002”. (2001年8月31日) 2006年12月15日閲覧。
- ^ Eichar, Douglas (1989). Occupation and Class Consciousness in America. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-26111-3
- ^ Thompson, William; Joseph Hickey (2005). Society in Focus. Boston, MA: Pearson. ISBN 0-205-41365-X
- ^ Eichar, Douglas (1989). Occupation and Class Consciousness in America. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-26111-3
- ^ “Harvard Magazine, Middle class squeeze”. 2006年12月13日閲覧。
- ^ Ehrenreich, Barbara (1989). Fear of Falling, The Inner Life of the Middle Class. New York, NY: Harper Collins. ISBN 0-06-097333-1
- ^ “Blacks Are More Socially Conservative Than Barack Obama - Bonnie Erbe”. usnews.com (2008年11月7日). 2012年6月3日閲覧。
- ^ Davis, George (January 6, 2010). “Spiritually Liberal, Socially Conservative”. Psychology Today.
- ^ “U.S. Bureau of Labor, hours worked, 2005”. 2006年12月15日閲覧。
- ^ “U.S. Department of Labor, employment in 2006”. 2006年12月15日閲覧。
- ^ “International vacation comparison”. 2006年12月15日閲覧。
- ^ a b c d e Hine, Darlene; William C. Hine; Stanley Harrold (2006). The African American Odyssey. Boston, MA: Pearson
- ^ “U.S. Census Bureau, Race and Hispanic or Latino during the 2000 Census”. 2006年12月15日閲覧。
- ^ Semiannual Report of the War Relocation Authority, for the period January 1 to June 30, 1946, not dated. Papers of Dillon S. Myer. Scanned image at trumanlibrary.org. Accessed September 18, 2006.
- ^ “Religion in the U.S. by state”. USA Today 2006年12月14日閲覧。
- ^ a b “U.S. Census Bureau, Income newsbrief 2004”. 2006年12月11日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2006年12月15日閲覧。
- ^ “U.S. Census Bureau, educational attainment in the U.S. 2003” (PDF). 2006年12月15日閲覧。
- ^ “U.S. Department of Justice, Crime and Race”. 2006年12月12日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2006年12月15日閲覧。
- ^ http://www.adc.org/PDF/hcr02.pdf
- ^ “The Italian Way of Death”. Salon. 3 May 2009時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2009年10月8日閲覧。
- ^ Bunting, Bainbridge; Robert H. Nylander (1973). Old Cambridge. Cambridge, Mass.: Cambridge Historical Commission. p. 69. ISBN 0-262-53014-7
- ^ Brian K. Williams, Stacy C. Sawyer, Carl M. Wahlstrom, Marriages, Families & Intimate Relationships, 2005
- ^ a b “B02001. RACE – Universe: TOTAL POPULATION”. 2008 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. United States Census Bureau. 25 August 2010時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。February 28, 2010閲覧。
- ^ a b “Detailed Tables - American FactFinder; T4-2008. Hispanic or Latino By Race [15]”. 2008 Population Estimates. U.S. Census Bureau. 2010年2月28日閲覧。
- ^ “Detailed Tables - American FactFinder; T3-2008. Race [7]”. 2008 Population Estimates. U.S. Census Bureau. 2010年2月28日閲覧。
- ^ Imani Perry, More Beautiful More Terrible: The Embrace and Transcendence of Racial Inequality in the United States, New York University Press: 2011, p7
- ^ Perry, 21
- ^ “National Survey of Drug Use and Health”. 24 November 2013閲覧。
- ^ Adams, J.Q.; Pearlie Strother-Adams (2001). Dealing with Diversity. Chicago, IL: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. ISBN 0-7872-8145-X
- ^ Crary, David (September 9, 2010). “Study finds Americans in generous mood”. Burlington, Vermont: Burlington Free Press. pp. 1A
- ^ “Federal Government Outlays by Function and Subfunction: 1962–2015 Fiscal Year 2011 (Table 3.2)”. United States Government Printing Office. 21 December 2010閲覧。
- ^ “Self-Reported Gun Ownership in U.S. Is Highest Since 1993”. gallup. (October 26, 2011)
- ^ “U.S. most armed country with 90 guns per 100 people”. Reuters. (August 28, 2007)
- ^ “Gun Ownership by State”. Washington Post
- ^ “Personal Safety Top Reason Americans Own Guns Today”. gallup. (October 28, 2013)
- ^ “The U.S. gun stock: results from the 2004 national firearms survey”. Injury Prevention Journal. Template:Cite webの呼び出しエラー:引数 accessdate は必須です。
関連文献
[編集]- Coffin, Tristam P.; Cohen, Hennig, (editors), Folklore in America; tales, songs, superstitions, proverbs, riddles, games, folk drama and folk festivals, Garden City, N.Y. : Doubleday, 1966. Selections from the Journal of American folklore.
- Marcus, Greil (2007). The Shape of Things to Come: Prophecy and the American Voice. Macmillan. ISBN 0-312-42642-9
- Shell, Ellen Ruppel, Cheap: The High Cost of Discount Culture, New York: Penguin Press, 2009. ISBN 978-1-59420-215-5
- Swirski, Peter. Ars Americana Ars Politica: Partisan Expression in Contemporary American Literature and Culture. Montreal, London: McGill-Queen's University Press (2010) ISBN 978-0-7735-3766-8
- Crunden, Robert Morse (1996). A Brief History of American Culture. M.E. Sharpe. p. 363. ISBN 9781563248658
外部リンク
[編集]- Customs & Culture in the U.S.
- American Culture Education
- Life in the USA: The Complete Guide for Immigrants and Americans
- Guide to American culture and customs for foreign students (U.S. Army Intelligence)
- CommonCensus Map Project – Identifying geographic spheres of influence
en:Template:Life in the United States












